Trending Digestion Topics
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is pain in the belly and can be acute or chronic. Abdominal pain can reflect a major problem with one of the organs in the abdomen such as the appendix, gallbladder, large and small intestine, pancreas, liver, colon, duodenum, and spleen.
Digestive Disorders Quiz
That stomach pain could be a digestive disease, you know. Why suffer? This quiz tests your knowledge of gastrointestinal symptoms that could be related to your tummy troubles.
Misconceptions About Digestion Slideshow
Watch this slideshow on digestive disease myths and learn about common misconceptions such as "Does spicy food cause ulcers?" and "Diverticulitis is an uncommon problem" to "Habitual use of enemas to treat constipation is harmless" and "Bowel regularity means a bowel movement every day."
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) causes symptoms and signs such as increased gas, cramping, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
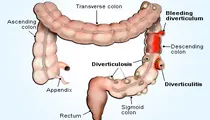
Diverticulitis
Watch this slideshow on diverticulitis (diverticulosis) - a condition in which the diverticulitum (small bulging sac) or diverticulita (more than one sac) rupture in the colon causing infection.
Bowel Disease
In this slideshow learn about inflammatory bowel disease which explains Crohn's and ulcerative colitis, including the symptoms, causes, testing, treatments, and home care needed to manage these types of IBD.
Related Disease Conditions
 12 Proven Ways to Reduce or Stop Bloating
12 Proven Ways to Reduce or Stop BloatingBloating is a condition where your abdomen feels full, tight, and distended often due to gas. Here are some scientifically proven ways to reduce bloating quickly.
 15 Foods That Cause Constipation
15 Foods That Cause ConstipationConstipation or the decrease in frequency and/or difficulty in passing stools (bowel movements) can be caused by a variety of problems. Check out these top 15 foods to avoid because they cause constipation. Some foods to avoid include white rice and bread, caffeine, bananas, alcohol, processed foods, and frozen dinners.
 28 Tips to Get Rid of Heartburn at Night
28 Tips to Get Rid of Heartburn at NightWhat to know about nighttime heartburn relief. Learn foods to avoid, lifestyle changes, and medications for heartburn.
 7 Home Remedies That Can Help Relieve Acid Reflux
7 Home Remedies That Can Help Relieve Acid RefluxWhat is acid reflux and how can you find relief? Learn what home treatments can help to relieve your symptoms.
 9 Food Poisoning Myths That Are Wrong
9 Food Poisoning Myths That Are WrongKnowing too much wrong information about a condition is just as bad as knowing too little about a disease. That's why we took it upon ourselves to debunk these 9 food poisoning myths.
 Abdominal Pain
Abdominal PainAbdominal pain can have many causes that range from mild to severe. Some of these causes include bloating, gas, colitis, endometriosis, food poisoning, GERD, IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), ovarian cysts, abdominal adhesions, diverticulitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, gallbladder disease, liver disease, and cancers. Signs and symptoms of the more serious causes include dehydration, bloody or black tarry stools, severe abdominal pain, pain with no urination or painful urination. Treatment for abdominal pain depends upon the cause.
 Achalasia
AchalasiaEsophageal achalasia is a disease of the esophagus that mainly affects young adults. Achalasia makes it difficult to swallow, can cause chest pain, and may lead to regurgitation. Here we discuss achalasia symptoms, surgery, treatment, and causes. Learn the definition of achalasia and what you can do to treat the disease.
 Anal Fissure
Anal FissureAn anal fissure is a small tear or cut in the skin lining of the anus. Pain and/or rectal bleeding during bowel movements are common symptoms of anal fissures. Treatment includes increasing liquid intake, using stool softeners, prescription medications, and surgery.
 Anal Itching
Anal ItchingAnal itching is the irritation of the skin at the exit of the rectum, known as the anus, accompanied by the desire to scratch. Causes include everything from irritating foods we eat, to certain diseases, and infections. Treatment options include over-the-counter medications, using moist pads, and gentle cleaning and drying of the anus.
 Antiemetics
AntiemeticsNausea and vomiting after eating are symptoms that may be caused by many conditions. Antiemetics are drugs that help get rid of nausea and vomiting. Though some antiemetics for motion sickness and mild nausea remedies are available over the counter (OTC), most require a medical evaluation and prescription. Read experts describing what causes nausea and how to stop nausea and vomiting.
 Appendicitis
AppendicitisAppendicitis, or inflammation of the appendix, has many different causes. Pain in the abdomen is the most common symptom, but you also may experience nausea, vomiting, constipation, and fever. Learn about treatment and surgery.
 Are Bananas Bad for Kidneys?
Are Bananas Bad for Kidneys?Bananas are not bad for the kidneys unless the kidneys are damaged. Damaged kidneys build up potassium in the blood, resulting in serious heart problems. Potassium is present in bananas, other fruits and vegetables (such as potatoes, avocados and melons). People with advanced kidney disease are usually advised to avoid some fruits and vegetables, including bananas. Apart from this, bananas are safe and healthy to eat.
 Are Eggs Bad for Pancreatitis?
Are Eggs Bad for Pancreatitis?Egg yolks may be bad for pancreatitis due to their high-fat content. However, egg yolks may be swapped for egg whites in a regular diet because they are low in fat. Although fatty foods, such as egg yolks, won’t damage the pancreas, they do contribute to high triglyceride levels that are a common risk factor for pancreatitis.
 Are Hiccups Good or Bad?
Are Hiccups Good or Bad?In most cases, hiccups are typically harmless and last for a short duration.
 Are Smelly Farts Healthy? Types of Farts
Are Smelly Farts Healthy? Types of FartsSmelly farts, flatulence, or flatus are a normal part of digestion. Farts are gas; the gas that you swallow while eating and the gases formed in the gut when the food is being broken down.
 Ascites
AscitesAscites (fluid retention) are an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, often caused by liver disease or cirrhosis, cancers, or heart failure. Learn about symptoms, types, and treatment.
 Average Life Expectancy After a Liver Transplant?
Average Life Expectancy After a Liver Transplant?Liver transplant (LT) simply means replacing a diseased liver with a healthy one. The new liver may be taken from a brain-dead person (cadaver) or given by a living relative.
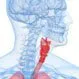 Barrett's Esophagus
Barrett's EsophagusBarrett's esophagus occurs as a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), primarily in white males. GERD refers to the reflux of acidic fluid from the stomach into the esophagus (the swallowing tube) and is classically associated with heartburn. Learn the symptoms, causes, and treatments for Barrett's esophagus.
 Beyond Food: What Triggers Heartburn and GERD?
Beyond Food: What Triggers Heartburn and GERD?Heartburn is the burning sensation in the chest due to backflow or reflux of the acidic stomach contents into the food pipe (esophagus). Heartburn is a major symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD.
 Bilirubin Test
Bilirubin TestBilirubin is a waste product of the normal breakdown of red blood cells in the liver. Normal bilirubin levels vary from lab to lab, and range from around 0.2 to 1.2 mg/dL. High levels of bilirubin can be diagnosed with a bilirubin blood test. Causes of elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood can be caused by infections, viral hepatitis, anemia, genetic diseases, and liver problems. Symptoms of elevated bilirubin levels depend on the cause; however, jaundice is a common sign. Treatment for elevated bilirubin levels depends on the cause.
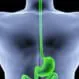 Bleeding Varices
Bleeding VaricesVarices are dilated blood vessels usually in the esophagus or stomach. Symptoms of bleeding varices include vomiting blood, black stools, low blood pressure, shock, and rapid heart rate. Bleeding varices are a medical emergency. Treatment may involve liver transplant, devascularization, distal splenorenal shunt, banding, sclerotherapy, or transjugular intrahepatic protosystemic shunt.
 Blood in the Stool (Rectal Bleeding)
Blood in the Stool (Rectal Bleeding)Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding (hematochezia) refers to the passage of bright red blood from the anus. Common causes include anal fissures, hemorrhoids, diverticulitis, colitis, Crohn's disease, colon and rectum polyps, and cancer. The color of the blood in the stool may provide information about the origin of the bleeding. The color of stool with blood in it may range from black, red, maroon, green yellow, gray, or white, and may be tarry, or sticky. Treatment of blood in the stool depends on the cause.
 Blood When I Wipe: 11 Causes of Rectal Bleeding
Blood When I Wipe: 11 Causes of Rectal BleedingOozing of blood from the anus or rectum during passing stools is called rectal bleeding. The blood may be from any part of the gut or even from stomach. The color of blood may vary depending on the site. Fresh red color is a sign of bleeding in the rectum or anus.
 Bowel Incontinence (Fecal Incontinence)
Bowel Incontinence (Fecal Incontinence)Bowel or fecal incontinence refers to the loss of voluntary control of stool, or bowel movements. The condition can include partial incontinence, in which a person loses only a small amount of liquid waste, to complete incontinence, in which the entire bowel movement cannot be controlled. Diet changes and the elimination of certain medications can help patients to regain bowel control. Treatment involves a combination of medication, biofeedback, and exercise.
 Can a Kidney Infection Cause Back Pain?
Can a Kidney Infection Cause Back Pain?Many people are affected by lower back pain. Learn how to tell if lower back pain is due to a kidney infection or the result of other causes.
 Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Cured?
Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Cured?Liver damage from mild alcoholic hepatitis can usually be cured by complete abstinence from alcohol and lifestyle changes. Learn about symptoms, treatment, and survival rates.
 Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Reversed?
Can Alcoholic Hepatitis Be Reversed?While mild alcoholic hepatitis may be reversed, once it reaches the stage of liver cirrhosis, it is irreversible. After diagnosis, abstaining from alcohol can improve your lifespan.
 Can Cholelithiasis Cause Cholecystitis?
Can Cholelithiasis Cause Cholecystitis?What is the difference between cholelithiasis and cholecystitis?
 Can Cranberry Pills Turn Your Urine Red?
Can Cranberry Pills Turn Your Urine Red?Cranberry pills have not been shown to turn the color of your urine red. Check out the center below for more medical references on bladder conditions, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Can Diverticulitis Cause Urinary Symptoms?
Can Diverticulitis Cause Urinary Symptoms?Diverticular disease and diverticulitis both affect the large intestine (bowel). Nausea and vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, and bladder symptoms such as pain or burning when peeing or the desire to urinate frequently are possible symptoms.
 Can Diverticulitis Go Away on Its Own?
Can Diverticulitis Go Away on Its Own?Yes, an attack of uncomplicated diverticulitis can go away on its own. However, you must visit your doctor for a thorough evaluation of the episode. Most attacks of uncomplicated diverticulitis are not life-threatening and usually resolve within a week. Complicated diverticulitis needs medical attention because it can cause serious complications.
 Can Gallstones Go Away on Their Own?
Can Gallstones Go Away on Their Own?The bile contents may sometimes crystallize and form gallstones. If there are no symptoms, a regular follow-up would suffice. Natural remedies and medical management may prevent worsening of the condition. Treatment is necessary if the stones cause pain or swelling of the gallbladder. Surgery may be required if nonsurgical treatments fail or there is a high risk of complications.
 Can Gastroenteritis Cause a High White Blood Cell Count?
Can Gastroenteritis Cause a High White Blood Cell Count?What is gastroenteritis, and does it cause a high white blood cell count? Learn the symptoms and causes of gastroenteritis.
 Can I Eat Mashed Potatoes 2 Days Before Colonoscopy?
Can I Eat Mashed Potatoes 2 Days Before Colonoscopy?Colonoscopy is a procedure used to detect abnormalities in the large intestine (colon). One day before the procedure, it is advised not to eat any solid or semi-solid food, such as mashed potatoes, applesauce, oatmeal, etc. A clear liquid diet must be taken 24 to 72 hours before the procedure.
 Can I Normally Eat 2 Days Before Colonoscopy?
Can I Normally Eat 2 Days Before Colonoscopy?In general, it is recommended to eat a low-fiber diet along with laxatives about 2-3 days before a colonoscopy so that your doctor can see potential problems more clearly.
 Can Urinary Incontinence Be Reversed?
Can Urinary Incontinence Be Reversed?Urinary incontinence can happen to anyone and the severity varies depending on the age, cause, and type of urinary incontinence. Most cases of urinary incontinence can be cured or controlled with appropriate treatment.
 Can You Eat Eggs When You Have Diarrhea?
Can You Eat Eggs When You Have Diarrhea?In most individuals with diarrhea, eggs help slow down bowel movements and help the patient recover faster from diarrhea. Cooking them makes them easier to digest.
 Can You Live a Normal Life After Donating a Kidney?
Can You Live a Normal Life After Donating a Kidney?Kidney donor surgery is considered a very low-risk surgery with few major complications. People who have donated a kidney can lead active and full lives.
 Can You Live With Stage I Kidney Disease?
Can You Live With Stage I Kidney Disease?Because you can halt further kidney damage with diet modification and supportive treatment, patients can live an extra 30 years following their stage I CKD diagnosis.
 Can You Live Without a Liver?
Can You Live Without a Liver?The liver is a vital organ regulating the levels of many substances in the body. It excretes a substance called bile. The bile helps in carrying away the waste from the liver. The blood from the digestive system (stomach and bowel) passes through the liver.
- Can You Poop With a Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse is the sliding down of the rectum (the last part of the large bowel) from its normal position and protruding out of the body. The prolapse may involve either the superficial lining or full thickness of the rectal wall sliding down through the anus. The degree of prolapse varies depending on the extent of the protrusion.
 Can You Recover From Stage II CKD?
Can You Recover From Stage II CKD?Since the kidneys can never heal themselves, there is no such thing as a full recovery from chronic kidney disease (CKD).
 Can You Still Poop With Impacted Feces?
Can You Still Poop With Impacted Feces?Digestion is the process of breaking down food in the gut so that it is in easily absorbable forms. The food travels from the mouth to the food pipe, stomach, small bowel, and large bowel to be finally eliminated through the anus. The small bowel (small intestine) absorbs nutrients from the food.
 Carcinoid Syndrome (Tumor)
Carcinoid Syndrome (Tumor)A carcinoid tumor is a tumor that develops from enterochromaffin cells. The important characteristic of carcinoid tumors that sets them apart from other gastrointestinal tract tumors, is their potential to cause the carcinoid syndrome. Local symptoms may include abdominal pain, intestinal bleeding, flushing., gastrointestinal bleeding, and diarrhea. Often, symptoms of the carcinoid syndrome can be more devastating than the local symptoms. There are many options for the treatment of carcinoid tumors and carcinoid syndrome.
 Celiac Disease
Celiac DiseaseCeliac disease is a condition in which a person has inflammation of the small intestinal mucosa when exposed to gluten in the diet. Symptoms of celiac disease include bloating, nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Treatment involves following a gluten-free diet. Some individuals may have refractory celiac disease in which they do not respond to a gluten-free diet.
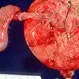 Choledochal Cyst
Choledochal CystCholedochal cysts are cysts of the bile ducts. There are several different types of choledochal cysts. These cysts are congenital, however, their cause is not known. Symptoms of choledochal cysts in infants include an enlarged liver and jaundice. In older people, the cysts cause abdominal pain, jaundice, cholangitis, gallstones, and pancreatitis. Treatment for choledochal cysts is surgery.
 Ciguatera Poisoning
Ciguatera PoisoningCiguatera poisoning is a type of food poisoning caused by the ciguatera toxin found in a variety of large reef fish found between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. Symptoms of ciguatera poisoning include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, vertigo, numbness, tingling, and muscle pain. Ciguatera poisoning requires medical treatment.
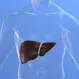 Cirrhosis
CirrhosisCirrhosis of the liver refers to a disease in which normal liver cells are replaced by scar tissue caused by alcohol and viral hepatitis B and C. This disease leads to abnormalities in the liver's ability to handle toxins and blood flow, causing internal bleeding, kidney failure, mental confusion, coma, body fluid accumulation, and frequent infections.</p><p> Symptoms include yellowing of the skin (jaundice), itching, and fatigue. The prognosis is good for some people with cirrhosis of the liver, and the survival can be up to 12 years; however, the life expectancy is about 6 months to 2 years for people with severe cirrhosis with major complications.
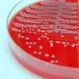 Clostridium Difficile Colitis
Clostridium Difficile ColitisClostridium difficile (C. difficile) is a bacterium, and is one of the most common causes of infection of the colon. C. difficile spores are found frequently in hospitals, nursing homes, extended care facilities, and nurseries for newborn infants.
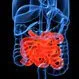 Colitis
ColitisColitis refers to inflammation of the inner lining of the colon. Symptoms of the inflammation of the colon lining include diarrhea, pain, and blood in the stool. There are several causes of colitis, including infection, ischemia of the colon, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, infectious colitis like C. difficile, or microscopic colitis). Treatment depends on the cause of the colitis.
 Colon Polyps
Colon PolypsColon polyps are fleshy growths inside the colon lining that may become cancerous. Symptoms include rectal bleeding. Learn about causes, signs, treatment, and how to prevent colon cancer.
 Constipation
ConstipationConstipation is defined medically as fewer than three stools per week and severe constipation as less than one stool per week. Constipation usually is caused by the slow movement of stool through the colon. There are many causes of constipation including medications, poor bowel habits, low-fiber diets, laxative abuse, hormonal disorders, and diseases primarily of other parts of the body that also affect the colon.
 Crohn's Disease
Crohn's DiseaseCrohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease, primarily involving the small and large intestines, but it can affect other parts of the digestive system as well. Abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and weight loss are common symptoms and signs.
 Crohn's Disease vs. Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn's Disease vs. Ulcerative ColitisCrohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are diseases that cause inflammation of part of or the entire digestive tract (GI). Crohn's affects the entire GI tract (from the mouth to the anus), while ulcerative colitis or ulcerative colitis only affects the large and small intestines and ilium. Researchers do not know the exact cause of either disease. About 20% of people with Crohn's disease also have a family member with the disease. Researchers believe that certain factors may play a role in causing UC. Both Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are a type of inflammatory bowel disease or IBD. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis both have similar symptoms and signs, for example, nausea, loss of appetite, fatigue, weight loss, episodic and/or persistent diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain and cramping, rectal bleeding, bloody stools, joint pain and soreness, eye redness, or pain.
 Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome (CVS)
Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome (CVS)Cyclic vomiting syndrome is a condition in which affected individuals have severe nausea and vomiting that come in cycles. Researchers believe that cyclic vomiting syndrome and migraine headaches are related. Triggers of cyclic vomiting syndrome are emotional stress and infections. People with cyclic vomiting syndrome are at an increased risk of dehydration. Cyclic vomiting syndrome is difficult to diagnose. Treatment varies from person to person but is generally directed toward relief of the condition's symptoms.
 Diarrhea
DiarrheaDiarrhea is a change in the frequency and looseness of bowel movements. Symptoms associated with diarrhea are cramping, abdominal pain, and the sensation of rectal urgency. Causes of diarrhea include viral, bacterial, or parasite infection, gastroenteritis, food poisoning, and drugs. Absorbents and anti-motility medications are used to treat diarrhea.
 Direct vs. Indirect Hernia
Direct vs. Indirect HerniaDirect and indirect hernia are both inguinal hernias. Both types of hernias may cause a visible bulge in the groin area. Weakness in the muscle of the abdominal wall causes a direct hernia. A birth defect causes an indirect hernia. Hernias that can't be pushed in need surgery.
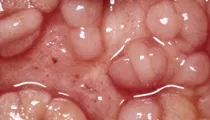
 Diverticulosis
DiverticulosisMost people with diverticulosis have few if any symptoms at all. When people do experience signs and symptoms of diverticulosis (diverticular disease) they may include abdominal pain, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, constipation, and bloating. Diverticulitis is a condition in which the diverticula in the colon ruptures. The rupture results in infection in the tissues that surround the colon. Treatment methods for diverticulitis include prescription medications, and in some cases, diverticulitis surgery.
 Diverticulosis vs. Diverticulitis
Diverticulosis vs. DiverticulitisIn many cases, diverticulosis is asymptomatic. The condition may go undiagnosed till a routine colonoscopy is done. However, in a few individuals, diverticulitis causes symptoms - referred to as a diverticulitis attack or flare-up.
 Do Stomach Ulcers Go Away on Their Own?
Do Stomach Ulcers Go Away on Their Own?Some stomach ulcers may go away on their own without treatment, especially if you follow a strict diet and avoid triggers. However, ulcers can worsen if left untreated.
 Do Stomach Ulcers Go Away?
Do Stomach Ulcers Go Away?Stomach ulcers are sores on the inner lining of the stomach. Stomach ulcer symptoms may go away after some time, but the ulcer may still be there.
 Does Crohn's Disease Weaken Your Immune System?
Does Crohn's Disease Weaken Your Immune System?Studies show that Crohn's disease is the result of a weakened immune system; however, the extent of that weakness varies by patient.
 Does Drinking Water Help Diverticulitis?
Does Drinking Water Help Diverticulitis?Yes, drinking water may help resolve diverticulitis. However, the overall management of diverticulitis depends on the extent of the disease. Only hydration may not help in all cases. It is advised to maintain a liquid diet, such as clear liquids or broths, during the first few days of the diverticulitis attack. This is because constipation is a major cause of diverticulitis.
 Does Giardia Go Away on Its Own?
Does Giardia Go Away on Its Own?Mild infections of giardiasis parasites may clear up on their own in a few weeks. However, more severe cases of giardia may cause long-term symptoms and complications.
 Does Pushing a Hemorrhoid Back in Help?
Does Pushing a Hemorrhoid Back in Help?Hemorrhoids are very common and appear when the veins under the lining of the rectum and anus become swollen and bulge. Yes, you can push a hemorrhoid back in.
 Does Sprite Help With Diarrhea?
Does Sprite Help With Diarrhea?Diarrhea causes the body to lose fluids, leading to dehydration. Sugary drinks, such as Sprite, may not be high up on the list of recommended fluids in case of diarrhea. If you don't have any other options but to drink Sprite, it may be a good idea to add some water to it and let the bubbles fizz out before drinking it.
 Does Tobacco Increase Stomach Acid?
Does Tobacco Increase Stomach Acid?Tobacco use, whether smoking cigarettes or chewing tobacco, causes the stomach to make more acid, which increases the risk of acid reflux.
 Does Your Digestive System Change With Age?
Does Your Digestive System Change With Age?As you age, your digestive system can slow down and become less efficient, leading to constipation, heartburn, and other digestive problems.
 Does Your Digestive System Slow Down as You Get Older?
Does Your Digestive System Slow Down as You Get Older?Your digestive system can slow down as you get older, with muscles in the digestive tract becoming weaker and less efficient in breaking down foods.
 Drug-Induced Liver Disease
Drug-Induced Liver DiseaseDrug-induced liver diseases are diseases of the liver that are caused by physician-prescribed medications, OTC medications, vitamins, hormones, herbs, illicit (recreational) drugs, and environmental toxins. Read about the signs and symptoms of drug-induced liver disease like hepatitis (inflammation of the liver cells), liver disease treatment, and types.
 Duodenal Diverticulum
Duodenal DiverticulumDuodenal diverticula (extramural or intramural), or duodenal diverticulum, is a pouch that is attached to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum). The cause of extramural diverticula is not clear, however, it may be congenital. Complications caused by duodenal diverticulum include rupture, gallstones, or pancreatitis. Extramural duodenal diverticula has no symptoms. Treatment is generally surgery.
 Dyspepsia (Indigestion)
Dyspepsia (Indigestion)Indigestion (dyspepsia, upset stomach) can be caused by problems related to, or not related to the gastrointestinal tract. Signs and symptoms are upper abdominal pain, belching, nausea, vomiting, abdominal bloating, and abdominal distention. Treatment depends upon the cause.
 E. coli (0157:H7) Infection
E. coli (0157:H7) InfectionThere are many types of E. coli (Escherichia coli). E. coli can cause urinary tract and bladder infections, or lead to sepsis. E coli O157:H7 (EHEC) causes bloody diarrhea and colitis. Complications of E. coli infection include hemorrhagic diarrhea, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Symptoms include severe abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. E coli O157:H7 commonly is due to eating raw or undercooked hamburgers or raw milk or dairy products.
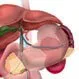 Enlarged Spleen
Enlarged SpleenAn enlarged spleen or splenomegaly is generally caused by other diseases or conditions such as infections, cancers, blood disorders, or decreased blood flow. Symptoms of an enlarged spleen are often unnoticed. A feeling of fullness after eating a small amount of food and not being able to eat large meals may be a symptom of an enlarged spleen. Treatment for an enlarged spleen depends upon the cause.
 Enterovirulent E. coli (EEC)
Enterovirulent E. coli (EEC)Enterovirulent Escherichia coli (E. coli) are strains of related bacteria that have a strong propensity to cause gastrointestinal tract infections. Examples of strains include EHEC (enterohemorrhagic E. coli), ETEC (enterotoxigenic E. coli), EPEC (enteropathogenic E. coli), EIEC (enteroinvasive E. coli), EAEC (enteroadherent E. coli), and EAggEC (enteroaggregative E. coli). Symptoms may vary depending on the strain the individual contracts. Infection is spread generally through contaminated food or drink.
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic EsophagitisEosinophilic esophagitis is an inflammation of the esophagus. Eosinophilic esophagitis has many causes including acid reflux, heartburn, viruses, medications that become stuck in the esophagus, allergy, asthma, hay fever, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. Eosinophilic esophagitis symptoms include difficulty swallowing food, abdominal pain, chest pain, and heartburn.
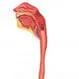 Esophagitis
EsophagitisEsophagitis is caused by an infection or irritation of the esophagus. Infections that cause esophagitis include a candida yeast infection of the esophagus as well as herpes. Signs and symptoms of esophagitis include cough, mouth sores, chest pain, bad breath, sore throat, heartburn, and difficulty swallowing. Treatment of esophagitis includes diet, lifestyle changes, and medication depending upon the cause.
 Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency or EPI is a condition in which a person's pancreas can't produce or secrete certain enzymes into the gastrointestinal tract, which results in the inability to digest and absorb some minerals, vitamins, and fats from food. Symptoms of EPI include diarrhea, bloating, excessive gas, bone pain, and foul smelling bowel movements. Treatment for EPI is PERT therapy.
 Fatty Liver
Fatty LiverNonalcoholic fatty liver disease or NASH occurs due to the accumulation of abnormal amounts of fat within the liver. Fatty liver most likely caused by obesity and diabetes. Symptoms of fatty liver disease are primarily the complications of cirrhosis of the liver; and may include mental changes, liver cancer, the accumulation of fluid in the body (ascites, edema), and gastrointestinal bleeding. Treatment for fatty liver includes avoiding certain foods and alcohol. Exercise, weight loss, bariatric surgery, and liver transplantation are treatments for fatty liver disease.
 Food Poisoning
Food PoisoningFood poisoning is common but can also be life-threatening. Food poisoning symptoms include stomach cramps, diarrhea, and vomiting. Read about different types of food poisoning, treatment, and tips for prevention.
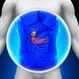 Gallbladder Pain (Gall Bladder Pain)
Gallbladder Pain (Gall Bladder Pain)Gallbladder pain (often misspelled "gall bladder") is generally produced by of five problems, biliary colic, cholecystitis, gallstones, and pancreatitis. Causes of gallbladder pain include intermittent blockage of ducts by gallstones or gallstone inflammation and/or sludge that also may involve irritation or infection of surrounding tissues, or when a bile duct is completely blocked. Treatment of gallbladder depends on the cause, which may include surgery.
 Gallstones
GallstonesGallstones are stones that form when substances in the bile harden. Gallstones (formed in the gallbladder) can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. There can be just one large stone, hundreds of tiny stones, or any combination. The majority of gallstones do not cause signs or symptoms; however, when they do occur the primary sign is biliary colic. Symptoms of biliary colic are constant pain for 15 minutes to 4-5 hours, and it may vary in intensity; nausea, severe pain that does not worsen with movement; and pain beneath the sternum. Treatment of gallstones depends upon the patient and the clinical situation.
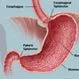 Gastritis
GastritisGastritis (acute and chronic) is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach Some people have no gastritis symptoms, but when they do occur they may include bloating, belching, loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. <i>H. pylori</i> infection and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the two main causes of gastritis. Alcohol, caffeine, and high-fat foods also can cause gastritis. Fried, fatty, and spicy foods and alcohol aggravate gastritis symptoms. Other stomach lining irritants that aggravate symptoms include cigarette smoking, acidic juices, caffeine, tomato products, peppers, and chili powder. Foods that soothe gastritis symptoms, and that help reduce and stop <i>H. pylori</i> infection growth in the stomach includes apples, onions, garlic, teas, green leafy vegetables, coconut water, and wheat bran. Gastritis is diagnosed with endoscopy, blood tests, or stool tests. Some people get relief from gastritis symptoms with prescription and non-prescription antacids, histamine blockers like famotidine (Pepcid AC) or ranitidine (Zantac 75), or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) like omeprazole (Prilosec) and esomeprazole (Nexium). These drugs will not cure gastritis. Complications of gastritis include gastric cancers, MALT lymphoma, renal problems, and death.
 Gastroenteritis
GastroenteritisStomach flu (gastroenteritis) is a term referred used to describe a variety of gastrointestinal problems. The most common signs and symptoms of gastroenteritis are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. The most common cause of gastroenteritis in the United States is <i>Norovirus</i>. Other causes of gastroenteritis include <i>Rotavirus, Astrovirus, Adenovirus,</i> and <i>Sapovirus</i>. There are bacterial causes of gastroenteritis such as <i>Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter Aeromonas, E. coli, Clostridium, Vibrio, Campylobacter</i>, and <i>Yersinia spp</i>. Parasites that cause gastroenteritis include <i>Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora</i>, and <i>Entamoeba</i>. Treatment for gastroenteritis is generally home remedies such as keeping hydrated to prevent dehydration. At times, hospitalization may be necessary if dehydration occurs.
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also called acid reflux, can cause symptoms like heartburn, chest pain, regurgitation, and nausea. Learn about causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
 Gastroparesis
GastroparesisGastroparesis is a medical condition in which the muscle of the stomach is paralyzed by a disease of either the stomach muscle itself or the nerves controlling the muscle. As a consequence, food and secretions do not empty normally from the stomach. Gastroparesis symptoms are nausea and vomiting; abdominal bloating, and pain can result.
 Gastroparesis diet: Food to Avoid & Food to Eat
Gastroparesis diet: Food to Avoid & Food to EatThe goal of the gastroparesis diet is to decrease distressing gastrointestinal symptoms while managing an intake of adequate fluids and nourishment.
 GERD in Infants and Children
GERD in Infants and ChildrenGERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) is the upward movement of stomach content, including acid, into the esophagus and sometimes into or out of the mouth. Common symptoms of GERD in children include colic, feeding problems, poor growth, frequent vomiting or coughing, heartburn, regurgitation, recurrent wheezing, pneumonia, choking, or gagging. Treatment may involve elevating the child's bed, keeping the child upright after eating, limiting foods that seem to make the reflux worse, encouraging your child to exercise, and serving several small meals a day.
 GERD: Is the Damage Reversible?
GERD: Is the Damage Reversible?Gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD is caused by the weakening of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). LES is a group of muscles that act as a valve to prevent the acidic contents of the stomach from refluxing into the esophagus.
 Gilbert Syndrome
Gilbert SyndromeGilbert syndrome is a harmless genetic condition that causes abnormal breakdown of bilirubin, a compound that is formed when hemoglobin from red blood cells degrades. High bilirubin can cause jaundice (yellowing of the eyes). Gilbert syndrome does not need to be treated and has a good prognosis.
 Heartburn
HeartburnHeartburn is a burning sensation experienced from acid reflux (GERD). Symptoms of heartburn include chest pain, burning in the throat, difficulty swallowing, the feeling of food sticking in the throat, and a burning feeling in the chest. Causes of heartburn include dietary habits, lifestyle habits, and medical causes. Treatments for heartburn include lifestyle changes, OTC medication, prescription medication, and surgery.
 Heartburn vs. Acid Reflux: What's the Difference?
Heartburn vs. Acid Reflux: What's the Difference?Heartburn and acid reflux are not the same thing. Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux. Heartburn gets its name because it feels like a burning sensation around the heart. Another symptom that occurs with heartburn is a bitter or sour taste in the mouth, usually when you eat or lie down. Heartburn affects more than 60 million people in the US at least once a month.
 Helicobacter Pylori
Helicobacter PyloriHelicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacteria that causes chronic inflammation (gastritis) of the inner lining of the stomach and also is the most common cause of ulcers worldwide. About 50% of people in the world carry or are infected with H. pylori. Common symptoms of H. pylori infection are occasional abdominal discomfort, bloating, belching or burping, and nausea and vomiting. H. pylori infection is difficult to eradicate, and treatment is with two or more antibiotics.
 Hemorrhoids
HemorrhoidsHemorrhoids (piles) are swollen veins in the rectum and anus. Causes include pregnancy, obesity, diarrhea, a low-fiber diet, and prolonged sitting on the toilet. Treatment varies depending on the severity of the hemorrhoids. Some treatment options include over-the-counter creams and suppositories, stool softeners, warm sitz baths, and hemorrhoidectomies.
 Hepatitis C
Hepatitis CHepatitis C is an inflammation of the liver due to the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which is usually spread by blood transfusion, hemodialysis, and needle sticks, especially with intravenous drug abuse. Symptoms of chronic hepatitis include fatigue, fever, muscle aches, loss of appetite, and fever. Chronic hepatitis C may be cured in most individuals with drugs that target specific genomes of hepatitis C.
 Hepatitis C Cure
Hepatitis C CureHepatitis is inflammation of the liver. There are a variety of toxins, diseases, illicit drugs, medications, bacterial and viral infections, and heavy alcohol use that can cause inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis C viral infection (HCV) is one type of hepatitis. According to the CDC, in 2014 there were an estimated 30,500 cases of acute hepatitis C infections in the US. An estimated 2.7-3.9 million people in the US have chronic hepatitis C. The virus is spread from person to person via blood-to-blood contact. Hepatitis C can be cured with medications in most people. There is no vaccine against the hepatitis C virus.
 Hepatitis E Viral Infection
Hepatitis E Viral InfectionHepatitis E is a viral infection caused by the hep E virus. Symptoms of hep E infection are pain in the right side if the abdomen, stool changes, jaundice, and brown or dark urine. Hep E is very serious for pregnant women. The hepatitis E virus is transmitted via the fecal-oral route from eating contaminated foods or drinks. There is no vaccine or cure for hep E infection in the U.S.
 Hepatitis Immunizations
Hepatitis ImmunizationsHepatitis A and hepatitis B are the two most common viruses that infect the liver. Hepatitis A and hepatitis B can be prevented and treated with immunizations (vaccinations) such as Havrix, Vaqta, Twinrix, Comvax, Pediarix, and hepatitis b immune globulin (HBIG).
 Hereditary Hemochromatosis (Iron Overload)
Hereditary Hemochromatosis (Iron Overload)Hereditary hemochromatosis (iron overload) is an inherited disorder in which there is excessive accumulation of iron in the body. Check out the center below for more medical references on hemochromatosis, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Hernia
HerniaA hernia occurs when an organ or piece of tissue protrudes from the space in which it is normally contained. Symptoms of a hernia include pain, nausea, vomiting, bowel obstruction, and fever. Hernias are diagnosed by a physical exam and imaging tests. Some hernias may be held in place with a supportive belt. Other hernias require surgical repair. The prognosis of people who undergo elective hernia repair tends to be good.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
 10 Dietary Changes to Help Manage Your UC
10 Dietary Changes to Help Manage Your UCFind out how to manage your UC by making changes to your diet.
 10 Fast Acting Ways to Relieve Heartburn
10 Fast Acting Ways to Relieve HeartburnWhat do you need to know about heartburn remedies? Learn the foods that cause heartburn, quick home remedies, and the rules of avoiding heartburn pain. Should you try aloe juice or apple cider vinegar for heartburn? Find out here.
 10 Ways to Maintain an Active Social Life When You Have UC
10 Ways to Maintain an Active Social Life When You Have UCFind out how you can remain socially active while managing ulcerative colitis.
 10 Ways to Manage Your Stress About UC
10 Ways to Manage Your Stress About UCDiscover the best ways to manage your stress when you have ulcerative colitis. Learn how techniques like yoga, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help your UC symptoms.
 Appendicitis Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Appendicitis Quiz: Test Your Medical IQHow dangerous is appendicitis? Take this quiz to answer questions, get quick facts, and learn the causes of appendicitis as well as symptoms, risks, and treatments for this common condition.
 Appendicitis: Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Appendectomy in Detail
Appendicitis: Symptoms, Signs, Causes, Appendectomy in DetailWhat causes appendicitis? What causes a burst or ruptured appendix? Learn step-by-step what happens during laparoscopic appendectomy. Find appendectomy recovery time, early appendicitis warning signs, and what the appendix's functions are. Know the appendicitis symptoms like pain in the abdomen.
 Celebrities With Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
Celebrities With Ulcerative Colitis (UC)Anybody can get ulcerative colitis. Here are some well-known people who were diagnosed with UC.
 Celiac Disease Quiz: What Is Celiac Disease?
Celiac Disease Quiz: What Is Celiac Disease?Could celiac disease be the cause of your tummy troubles? Take the Celiac Disease Quiz to learn what certain foods may be doing to your insides. Learn symptoms to look for as well as how to treat this digestive disorder.
 Celiac Disease: Symptoms, Gluten in Foods, Gluten Allergy Tests, and More
Celiac Disease: Symptoms, Gluten in Foods, Gluten Allergy Tests, and MoreDo you suffer from celiac disease? Learn about diet, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments for this digestive disorder that occurs in reaction to gluten and damages the intestines.
 Constipation: Foods to Eat, Foods to Avoid
Constipation: Foods to Eat, Foods to AvoidTake this quiz to find out what foods to eat, and what foods to avoid to prevent or relieve constipation.
 Crohn's Disease Quiz
Crohn's Disease QuizWhat causes Crohn's disease? What are the symptoms of Crohn's disease? How is Crohn's treated? Take this quiz to get the facts about Crohn's.
 Crohn's Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diet
Crohn's Disease: Symptoms, Causes, DietWhat is Crohn's disease? Get more information on this digestive disorder and how Crohn's can affect your diet. Learn more about tests to diagnose Crohn's disease, as well as treatments for Crohn's.
 Delicious, Not Dull: Tasty Diet Tips for IBD
Delicious, Not Dull: Tasty Diet Tips for IBDWant to know what to eat -- and what not to eat -- if you have ulcerative colitis? Check out these tips and delicious IBD-friendly recipes from WebMD.
 Diet and Nutrition: Foods to Help You Ease Bloating
Diet and Nutrition: Foods to Help You Ease BloatingGot bloat? These foods may help prevent extra air in your abdomen.
 Diet and Weight Loss: What's an Elimination Diet?
Diet and Weight Loss: What's an Elimination Diet?Ever wonder if a certain food causes your headaches or makes you tired or uncomfortable? You might try to find out with an elimination diet.
 Diet and Weight Loss: Why Are You Always Hungry?
Diet and Weight Loss: Why Are You Always Hungry?What are the causes of hunger? There are more reasons you get hungry than just an empty stomach. Food cravings, pregnancy, blood sugar spikes, lack of protein in the diet, smelling delicious foods, and eating while stressed or emotional are just a few causes of hunger. Learn about the hunger cues your body relies on to be fed.
 Digestive Disorders: 23 Constipation Myths and Facts
Digestive Disorders: 23 Constipation Myths and FactsConstipation results in fewer bowel movements. Laxatives, home remedies, and diet changes may bring constipation relief. Change habits that constipate you and adopt lifestyle changes to benefit your intestines and bowel. Bloating and chronic constipation are relieved with the right medical treatments.
 Digestive Disorders: Common Misconceptions
Digestive Disorders: Common MisconceptionsLearn about the digestive system and common misconceptions of digestive disorders. Read about what causes ulcers, heartburn, constipation, IBD, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and more.
 Digestive Disorders: How to Stop Gas Pain
Digestive Disorders: How to Stop Gas PainWhen gas gets stuck in your digestive system, you may feel pain or bloating. If changes in your diet or other habits don't fix it, you might need your doctor's help.
 Digestive Disorders: Reasons Your Stomach Hurts
Digestive Disorders: Reasons Your Stomach HurtsA belly ache can be a sign of so many things -- some serious, some not-so-serious. Check out a few possibilities.
 Digestive Disorders: Surprising Reasons Why You're Gassy
Digestive Disorders: Surprising Reasons Why You're GassyEveryone has some gas. But you might have more than usual because of these things. See what the culprits are.
 Digestive Disorders: Symptoms of Liver Problems
Digestive Disorders: Symptoms of Liver ProblemsBy the time a liver disease shows symptoms, it could already be advanced. Here are the signs to look for so you can stop the condition before it leads to liver failure.
 Digestive Disorders: Visual Guide to Stomach Ulcers
Digestive Disorders: Visual Guide to Stomach UlcersLearn about the causes and symptoms of stomach ulcers, and find out which kinds of treatment can help.
 Digestive Disorders: What to Eat (or Not) When Your Stomach Hurts
Digestive Disorders: What to Eat (or Not) When Your Stomach HurtsWe all get an upset stomach from time to time. Knowing what to eat -- and when -- can help keep you from feeling worse. Find out more from WebMD.
 Digestive Disorders: What You Should Know About Tapeworms
Digestive Disorders: What You Should Know About TapewormsHow much do you know about tapeworms? Find out more about what tapeworms are, how tapeworms get into your body, and how you can treat and prevent tapeworms.
 Digestive Disorders: What Your Poop Type and Color Mean
Digestive Disorders: What Your Poop Type and Color MeanThe different shapes and colors of your stool can tell you something about your health.
 Digestive Disorders: Why Do I Have Blood in My Stool?
Digestive Disorders: Why Do I Have Blood in My Stool?Do you have blood in your stool? Find out about possible causes and what steps you should take.
 Digestive Disorders: Worst Foods for Digestion
Digestive Disorders: Worst Foods for DigestionDiscover which foods to avoid in order to prevent diarrhea and digestive problems. Find out which foods can trigger diarrhea and other digestive problems such as gas, bloating, indigestion, heartburn and more.
 Digestive Health: 10 Probiotic Foods That Help Digestion
Digestive Health: 10 Probiotic Foods That Help DigestionProbiotics are beneficial bacteria and yeasts found in probiotic foods and fermented products like kimchi, kombucha, and kefir. Good bacteria may provide health benefits like weight loss and improved immunity. Lactobacillus is a type of probiotic bacteria. Learn the health benefits of yogurt.
 Digestive Health: Why Am I Bloated?
Digestive Health: Why Am I Bloated?Bloating is a sign and symptom of gas in the stomach or GI tract. Certain foods or health problems like constipation may cause it. Bacteria and certain foods like lactose can cause it. Learn the symptoms and causes of bloating to feel healthier.
 Diverticulitis (Diverticulosis) Symptoms, Diet, Treatment
Diverticulitis (Diverticulosis) Symptoms, Diet, TreatmentDiverticulitis (diverticulosis) is a condition in which the diverticulum or diverticula rupture in the colon, causing infection. Medical treatments such as antibiotics and surgery can treat diverticulitis (diverticulosis).
 GERD Quiz: Test Your Digestive Diseases IQ
GERD Quiz: Test Your Digestive Diseases IQWho is at risk for developing GERD? Are you? Take this quiz to learn what GERD is, if you're at risk, and what you can do about it.
 Heartburn: Foods to Eat, Foods to Avoid
Heartburn: Foods to Eat, Foods to AvoidLearn the symptoms of heartburn and which foods cause heartburn or GERD. Discover home remedies and which foods may provide treatment for heartburn relief.
 Hemorrhoids Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ of Piles
Hemorrhoids Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ of PilesDoes everyone have hemorrhoids? Test your knowledge of this and many other facts about Hemorrhoids.
 Hepatitis C Quiz: What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C Quiz: What is Hepatitis C?How many Americans have hepatitis C? Take this quiz to learn the facts about this chronic disease.
 Hernias: Causes, Types, and Treatments
Hernias: Causes, Types, and TreatmentsHernias often don't cause many symptoms, but they can lead to some serious problems. Use this WebMD slideshow to help yourself learn about what to look for and how they’re treated.
 How to Get Rid of Hemorrhoids: Types, Causes, and Treatments
How to Get Rid of Hemorrhoids: Types, Causes, and TreatmentsLearn how to get rid of hemorrhoids, the difference between internal hemorrhoids and external hemorrhoids, what causes hemorrhoids, how long hemorrhoids last, and hemorrhoids treatment.
 IBS - Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Symptoms, Diet, Treatment
IBS - Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Symptoms, Diet, TreatmentWhat is irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Learn about symptoms, causes, and foods that trigger IBS. Get lifestyle tips for managing IBS through diet and with IBS medications.
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentWhat is inflammatory bowel disease? IBD can include Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Learn more about testing, treatments, and the home care needed to manage inflammatory bowel disease.
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Quiz
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) QuizWhat are symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)? Take this quiz and get quick facts on causes and treatment options for this common and uncomfortable digestive disorder.
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The IBS Survival Kit
Irritable Bowel Syndrome: The IBS Survival KitIf you have IBS, you know that symptoms can show up at any time. WebMD's slideshow describes some things you can carry with you to be better prepared.
 Kidney Disease Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Kidney Disease Quiz: Test Your Medical IQKidney disease is common. Take this kidney disease quiz to test your knowledge and learn the symptoms, causes and types of kidney disease and what foods to eat and avoid!
 Kidney Stones: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Kidney Stones: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentWhat causes kidney stones? Where is kidney stone pain located on your body? Learn the symptoms and signs of kidney stone pain. Explore kidney stone treatment and how to prevent kidney stones.
 Lactose Intolerant? How to Get Calcium and Vitamin D
Lactose Intolerant? How to Get Calcium and Vitamin DSee how to eat right when dairy gives you stomach problems. WebMD shows you ways to get calcium and vitamin D through lactose-free milk, foods, and the sun.
 Liver Disease Quiz: Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis & Symptoms
Liver Disease Quiz: Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis & SymptomsWhat is liver disease? Take the Liver Disease Quiz and test your knowledge about this organ and its function.
 Nutritional Tips for Children and Teens with Ulcerative Colitis
Nutritional Tips for Children and Teens with Ulcerative ColitisThe symptoms of UC make it challenging for kids to get the proper nutrients. Try these tactics to help your child avoid symptom flares and get what their growing bodies need.
 Picture of Anus
Picture of AnusThe opening of the rectum to the outside of the body. See a picture of Anus and learn more about the health topic.
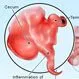 Picture of Appendicitis
Picture of AppendicitisInflammation of the appendix, the small worm-like projection from the first part of the colon. See a picture of Appendicitis and learn more about the health topic.
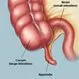 Picture of Appendix 1
Picture of Appendix 1Front View of the Appendix. The appendix sits at the junction of the small intestine and large intestine. See a picture of the Appendix and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Appendix 2
Picture of Appendix 2The appendix is a closed-ended, narrow, worm-like tube up to several inches in length that attaches to the cecum (the first part of the colon). See a picture of Appendix and learn more about the health topic.
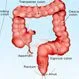
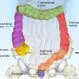 Picture of Colon
Picture of ColonThe part of the large intestine that serves to remove water from digested food and let the remaining material, solid waste called stool, move through it to the rectum and leave the body through the anus. See a picture of Colon and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Diverticulitis
Picture of DiverticulitisDiverticula can be seen via barium x-ray (barium enema). See a picture of Diverticulitis and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Diverticulosis
Picture of DiverticulosisDiverticulosis is a condition where a patient has diverticula in the colon. See a picture of Diverticulosis and learn more about the health topic.
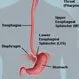 Picture of Esophagus
Picture of EsophagusThe esophagus is a muscular tube connecting the throat (pharynx) with the stomach. See a picture of the Esophagus and learn more about the health topic.
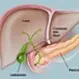 Picture of Gallbladder
Picture of GallbladderFront View of the Gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small pouch that sits just under the liver. See a picture of the Gallbladder and learn more about the health topic.
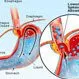 Picture of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD)
Picture of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD)The stomach contents regurgitate and back up (reflux) into the esophagus The food in the stomach is partially digested by stomach acid and enzymes. See a picture of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD) and learn more about the health topic.
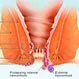 Picture of Hemorrhoid
Picture of HemorrhoidA dilated (enlarged) vein in the walls of the anus and sometimes around the rectum, usually caused by untreated constipation but occasionally associated with chronic diarrhea. See a picture of Hemorrhoid and learn more about the health topic.
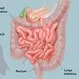 Picture of Intestines
Picture of IntestinesThe intestines are a long, continuous tube running from the stomach to the anus. See a picture of the Intestines and learn more about the health topic.
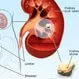 Picture of Kidney Stone
Picture of Kidney StoneA stone in the kidney (or lower down in the urinary tract). See a picture of Kidney Stone and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Kidney Stone Crystal
Picture of Kidney Stone CrystalKidney stones are made of salts and minerals in the urine that stick together, creating small "pebbles" formed within the kidney or urinary tract. See a picture of Kidney Stone Crystal and learn more about the health topic.
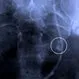 Picture of Kidney Stone Diagnosis
Picture of Kidney Stone DiagnosisThe diagnosis of kidney stones is suspected by the typical pattern of symptoms when other possible causes of the abdominal or flank pain are excluded. See a picture of Kidney Stone Diagnosis and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Lithotripsy
Picture of LithotripsyFor kidney stones that do not pass on their own, a procedure called lithotripsy is often used. See a picture of Lithotripsy and learn more about the health topic.
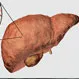
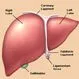 Picture of Liver
Picture of LiverFront View of the Liver. The liver is a large, meaty organ that sits on the right side of the belly. See a picture of the Liver and learn more about the health topic.
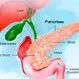 Picture of Pancreas
Picture of PancreasA fish-shaped spongy grayish-pink organ about 6 inches (15 cm) long that stretches across the back of the abdomen, behind the stomach. See a picture of the Pancreas and learn more about the health topic.
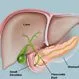 Picture of Pancreas Front View
Picture of Pancreas Front ViewFront View of the Pancreas. The pancreas is about 6 inches long and sits across the back of the abdomen, behind the stomach. See a picture of the Pancreas and learn more about the health topic.
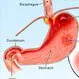 Picture of Peptic Ulcer
Picture of Peptic UlcerA hole in the lining of the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus. See a picture of Peptic Ulcer and learn more about the health topic.
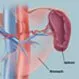 Picture of Spleen
Picture of SpleenFront View of the Spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper far left part of the abdomen, to the left of the stomach. See a picture of the Spleen and learn more about the health topic.
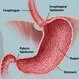 Picture of Stomach
Picture of StomachThe stomach is a muscular sac located on the left side of the upper abdomen. See a picture of the Stomach and learn more about the health topic.
 Pinworms Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication
Pinworms Symptoms, Treatments, and MedicationPinworm symptoms include itching and redness around the anus. Pinworm infection is common in children and adults. Pinworms are treated with over-the-counter medication. Your doctor can help confirm the diagnosis by checking for the presence of pinworms in stool.
 Stomach Pain Quiz: Nausea & Other Causes
Stomach Pain Quiz: Nausea & Other CausesTummy Troubles? Get a better idea of what's causing the nausea, vomiting, bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, pain, and other gastrointestinal discomforts and problems. Take the Tummy Troubles Quiz!
 Super Tips to Boost Digestive Health: Bloating, Constipation, and More
Super Tips to Boost Digestive Health: Bloating, Constipation, and MoreUpset stomach? Some foods may be the culprits, and bad habits may be to blame. Treat your body right with these simple nutrition tips on how to deal with with diarrhea, gas, reflux, and more digestive ailments.
 Ulcerative Colitis Quiz: Diet, Symptoms & Treatment
Ulcerative Colitis Quiz: Diet, Symptoms & TreatmentWhat is ulcerative colitis and what risks are associated with suffering over the long term? Take this Ulcerative Colitis Quiz to learn causes, symptoms, and treatments for this painful digestive disorder.
 Ulcerative Colitis Surgery -- What to Expect
Ulcerative Colitis Surgery -- What to ExpectSee the different surgeries used to treat ulcerative colitis. WebMD shows you when it may be needed, what is involved, and possible complications and benefits.
 Ulcerative Colitis: Symptoms, Diet, Treatment, Causes
Ulcerative Colitis: Symptoms, Diet, Treatment, CausesUlcerative Colitis is a form of inflammatory bowel disease and is slightly different than Crohn's disease. Learn the causes, symptoms, diet, and treatment options associated with ulcerative colitis.
Treatment & Diagnosis
- Antimitochondrial Antibodies
- Antro-duodenal Motility Study
- Appendectomy
- Balloon Endoscopy
- Barium Enema
- Blood Transfusion
- Can You Heal a Hernia Without Surgery?
- Capsule Endoscopy
- Cholecystectomy
- Cholescintigraphy
- Cologuard Test vs Colonoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Colostomy: A Patient's Perspective
- Creatinine Blood Test
- Dialysis
- Duodenal Biliary Drainage
- Electrogastrogram
- Electrolytes
- Endoscopic Ultrasound
- Endoscopy
- Endoscopy vs. Colonoscopy
- ERCP
- Esophageal Manometry Test
- Esophageal pH Monitoring
- Fecal Occult Blood Test
- Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
- Fundoplication
- Gastric Emptying Study Test
- How Do They Fix a Perforated Duodenal Ulcer?
- How Do You Replace a Gastrostomy Tube?
- How Do You Shrink Rectal Prolapse?
- How Is a Transjugular Liver Biopsy Done?
- How Is an Esophageal Manometry Performed?
- How Long Can You Leave a Biliary Stent In?
- How Long Does a Cholecystostomy Tube Stay In?
- How Long Does a Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication Last?
- How Long Does a Nissen Fundoplication Surgery Take?
- How Long Does an Exploratory Laparoscopy Take?
- How Long Does It Take for a Banded Hemorrhoid To Fall Off?
- How Long Does It Take for A Child to Recover from An Appendectomy?
- How Long Does It Take for a Saltwater Flush to Work?
- How Long Does It Take to Recover from A Gastrojejunostomy Procedure?
- How Long Does It Take to Recover From a Pancreas Surgery?
- How Long Does It Take to Recover From a Splenectomy?
- How Long Does It Take to Recover from An Appendectomy?
- Hydrogen Breath Test
- Intravenous Cholangiogram (IVC)
- Is a Loop Colostomy Permanent?
- Is an Anoscopy Painful?
- Is Capsule Endoscopy Safe?
- Is Heller Myotomy a Major Surgery?
- Is Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Major Surgery?
- Lactose Tolerance Test
- Liver Biopsy
- Liver Blood Tests: AST Normal Range, Results, Function
- Liver Resection
- Liver-Related Procedures and Tests
- Oral Cholecystogram
- Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
- Percutaneous Ethanol Injection of Liver
- Pinworm Test
- Push Endoscopy
- Sigmoidoscopy vs. Colonoscopy
- Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy
- Stool Acidity Test for Lactose Intolerance
- Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS)
- Upper GI Series
- Urea Breath Test
- Urinalysis
- Virtual Colonoscopy
- What Are the Types of Abdominal Incisions?
- What Does a Positive Occult Blood Test Indicate?
- What Is a Biliary Endoscopic Sphincterotomy?
- What Is a Choledochojejunostomy?
- What Is A Colon Resection?
- What Is a Gastrojejunostomy Procedure?
- What Is a Hepaticojejunostomy?
- What Is a Partial Gastrectomy?
- What Is an ALT Blood Test? Liver Function Test
- What Is an EGD Used to Diagnose?
- What Is an Open Appendectomy?
- What Is Braun Enteroesterostomy?
- What Is Distal Gastrectomy Surgery?
- What Is Fascial Closure?
- What Is Laparoscopic Right Colectomy?
- What Is Nasogastric Intubation Used For?
- What Is Open and Laparoscopic Resection Rectopexy?
- What Is Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage?
- What Is Recovery Time for Laparoscopic Appendectomy?
- What Is Rectal Foreign Body Removal Procedure?
- What Is SpyGlass Cholangioscopy?
- What Is the Difference Between Fluoroscopy and Radiography?
- What Is the Omentum?
- What Is the Pringle Maneuver Procedure?
- What Is the Purpose of a Vagotomy?
- What Is the Surgical Procedure for Pyloroplasty?
- Why Is a Spleen Removed in a Distal Pancreatectomy?
- Why Is an Exploratory Laparotomy Done?
Medications & Supplements
- Alka-Seltzer (sodium bicarbonate)
- alosetron (Lotronex)
- aluminum hydroxide
- aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, simethicone antacids
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide/simethicone
- aluminum hydroxide/magnesium trisilicate
- Anticholinergic and Antispasmodic Drugs
- artichoke
- atropine (Atreza)
- attapulgite
- Avsola (infliximab-axxq)
- balsalazide disodium (Colazal, Giazo)
- belladonna and opium (B and O Suppositories)
- bethanechol
- bifidobacterium
- bisacodyl
- bisacodyl (Dulcolax)
- bisacodyl rectal
- bisacodyl suppository and enema (Dulcolax, Biscolax)
- bismuth subsalicylate
- bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto Bismol, Kaopectate)
- blessed thistle
- boceprevir
- budesonide (Entocort EC, Uceris)
- calcitriol (Rocaltrol)
- calcium acetate (PhosLo)
- calcium carbonate antacid - oral, Dicarbosil, Rolaids, Titralac,
- Carbaglu (carglumic acid)
- castor oil
- chamomile
- chlordiazepoxide hydrochloride and clidinium bromide (Librax)
- cimetidine - oral, Tagamet
- cimetidine, Tagamet HB
- citric acid/sodium citrate
- citric acid/sodium citrate
- Colazal (balsalazide disodium) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- Colyte (peg-3350 and electrolytes)
- cordyceps
- Cortenema (hydrocortisone enema)
- defibrotide
- Dexilant (dexlansoprazole)
- dicyclomine, Bentyl
- digestive enzymes
- Digestive Enzymes Oral
- diphenoxylate and atropine (Lomotil)
- docusate
- docusate (Correctol, Colace, Dulcolax, Phillips Liquid-Gels, and many others)
- domperidone (oral)
- Doptelet (avatrombopag)
- Drax Exametazime
- Entyvio (vedolizumab)
- Epclusa (sofosbuvir and velpatasvir)
- esomeprazole (Nexium)
- esomeprazole delayed-release capsule - oral, Nexium
- esomeprazole delayed-release suspension - oral, Nexium
- etrasimod
- famotidine
- famotidine 10 mg - oral, Pepcid AC
- famotidine/calcium carbonate/magnesium hydroxide - chewable, Pepcid Complete
- fenugreek
- Givlaari (givosiran)
- GLUCAGON-INJECTION, Glucagon
- glutamine
- glycerin (Fleet, Pedia-Lax, Colace)
- glycerin rectal
- glycopyrrolate (Robinul, Cuvposa)
- gotu kola
- Helidac (bismuth subsalicylate/metronidazole/tetracycline hydrochloride)
- hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix, Vaqta)
- hepatitis b vaccine (Recombivax HB)
- horseweed
- hydrocortisone rectal
- hydrocortisone suppository - rectal, Anucort-HC, Anusol-HC, Cort-Do
- hydrocortisone, rectal suppository, enema, foam, Cortifoam, Anusol-HC, Anucort-HC, Proctocort
- hyoscyamine, atropine, scopolamine and phenobarbital (Donnatal)
- Ibsrela (tenapanor)
- Iceland moss
- infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra)
- juniper
- lactase enzyme
- Lactobacillus
- lactobacillus acidophilus
- lactulose
- lactulose laxative (Enulose, Generlac)
- lansoprazole (Heartburn Relief 24 Hour, Heartburn Treatment 24 Hour, Prevacid 24)
- lansoprazole delayed-release capsule - oral, Prevacid
- lansoprazole delayed-release disintegrating tablet - oral
- lansoprazole delayed-release suspension - oral, Prevacid
- ledipasvir and sofosbuvir
- lemon balm
- levocarnitine (Carnitor)
- levofloxacin (Levaquin) Side Effects and Adverse Effects
- licorice
- licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra)
- lidocaine rectal
- linaclotide (Linzess)
- loperamide
- lubiprostone (Amitiza)
- magaldrate
- magnesium citrate
Prevention & Wellness
- Bloating: 25 Foods and Drinks That Help Relieve Bloating Fast
- Does It Take 30 Minutes to Digest Food?
- How Do You Know If You Have Poor Digestion?
- How Long Should You Wait to Eat After Diarrhea?
- Is It Safe to Do an Enema at Home?
- Is Stomach Rumbling a Good Sign?
- Stomach Flu Remedies & What to Eat
- What Are the Signs You Need Probiotics?
- What Drinks Help Diarrhea?
- What Foods Are High in Oxalate (Oxalic Acid)?
- What Foods Trigger Ulcerative Colitis?
- What Fruit Is Good for Kidneys?
- What Helps Digestion After Overeating?
- What Is the Fastest Way to Detox Your Whole Body, and How Long Does It Take?