Trending Heart Topics
Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is caused by diseases (for example, heart disease, high blood pressure). Symptoms of CHF include fatigue, edema, shortness of breath, sleeplessness, and more. Treatments include lifestyle modifications, medications, heart transplant, and therapy.
Heart Disease Pictures Slideshow
Watch this slideshow of heart disease covering symptoms to watch for, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prevention strategies.
Heart Disease Quiz
Take our Heart Disease Quiz to get answers and facts about high cholesterol, atherosclerosis prevention, and the causes, symptoms, treatments, testing, and procedures for medically broken hearts.
Edema
Read about edema, an observable swelling in certain parts of the body. Edema may fall into one of two categories: pitting and non-pitting edema. Treatment for edema typically involves the use of diuretics.
Heart Symptoms Alert
Watch this slideshow on possible heart health symptoms never to ignore. Learn warning signs such as chest discomfort, rapid pulse, shortness of breath and more potential risk factors.
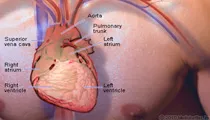
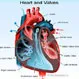
Heart Anatomy
View an illustration of the heart and see more medical anatomy and illustrations.
Related Disease Conditions
 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal Aortic AneurysmAn abdominal aortic aneurysm is an aneurysm (blood vessel rupture) in the part of the aorta that passes through the belly (abdomen). Learn about causes, symptoms, surgical and non-surgical treatments options, risks, and survival rates.
 Anemia
AnemiaAnemia (lack of blood) symptoms can vary depending on the cause. Symptoms may include fatigue, pale skin, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness. There are several anemia types. Anemia treatment depends upon the type.
 Angina Symptoms
Angina SymptomsClassic angina symptoms are described as chest pressure that radiates down the arm, into the neck or jaw and is associated with shortness of breath and sweating. Typical angina symptoms should be made worse with activity and should resolve or get better with rest. Angina may not have any pain and instead may present as shortness of breath with exercise, malaise, fatigue, or weakness.
 Aortic Dissection
Aortic DissectionAortic dissection is a small tear in the large blood vessel that leads from the heart and supplies blood to the body. Symptoms of aortic dissection include a tearing or ripping pain, nausea, sweating, weakness, shortness of breath, sweating, or fainting. Treatment depends on the type of aortic dissection, and the severity of the tear in the aorta.
 Aortic Stenosis
Aortic StenosisAortic stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the aortic valve in the heart. Symptoms include chest pain, fatigue, fainting, and shortness of breath and may be mild to severe. Read about the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of this condition.
 At What Age Does Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Develop?
At What Age Does Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Develop?Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or HCM is a medical condition that causes thickening of the heart muscles (the myocardium). It is a serious disorder that adversely affects the pumping of the heart and makes it prone to an abnormal rhythm. HCM is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death in individuals aged less than 30 years.
 Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a common heart rhythm abnormality with symptoms like dizziness, fainting, weakness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Types of AFib include paroxysmal and nonvalvular. Discover causes, symptoms, and effective treatment and management options to improve your heart health and find relief from AFib.
 Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Treatment Drugs
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Treatment DrugsAtrial fibrillation (AFib) is a heart rhythm disorder that causes irregular and often rapid heartbeat. The medications to treat AFib include beta-blockers, blood thinners, and heart rhythm drugs. Atrial fibrillation drugs can cause serious side effects like seizures, vision changes, shortness of breath, fainting, other abnormal heart rhythms, excessive bleeding while coughing or vomiting, blood in the stool, and bleeding into the brain.
 Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) vs. Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib)
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) vs. Ventricular Fibrillation (VFib)Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and ventricular fibrillation (VFib) are problems with the heart that cause abnormal heart rhythms. Check out the center below for more medical references on heart conditions, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Warning Symptoms
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) Warning SymptomsAtrial fibrillation or AFib is a type of heart rhythm abnormality. Early warning signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation include chest pain, palpitations, shortness of breath, and lightheadedness. Treatment for atrial fibrillation includes medical procedures, surgery, and medication.
 Atrial Flutter
Atrial FlutterAtrial flutter is a problem with the atria of the heart. In atrial flutter the atria of the heart rapidly and repeatedly beat due to an anomaly in the electrical system of the heart. It is a type of arrhythmia and can be dangerous because complications can develop easily. Signs and symptoms of atrial flutter include near fainting, palpitations, mild shortness of breath, and fatigue. While the exact cause of atrial flutter is not clearly understood, it's most likely related to your health, what medical conditions you certainly have, poor diet, lack of exercise, and drinking too much alcohol. Atrial flutter is diagnosed by physical examination, medical history, and a sawtooth ECG wave pattern.
 Atrial Flutter vs. Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Flutter vs. Atrial FibrillationAtrial flutter and atrial fibrillation (AFib) are two types of atrial tachycardia. Both of these conditions involve the heart's electrical activity, but they are not the same thing. Both of these diseases are serious and need medical treatment. Common symptoms of both conditions include palpitations, fatigue, chest pain, and blurry vision.
 Beta Thalassemia
Beta ThalassemiaBeta Thalassemia is the most familiar type of thalassemia. Thalassemia is not just one disease but rather a complex series of genetic (inherited) disorders all of which involve underproduction of hemoglobin. Beta thalassemia major symptoms include pale skin, irritability, growth retardation, swelling of the abdomen, and jaundice. Beta thalassemia treatments include directly relieving the symptoms of the illness.
 Blood Clots
Blood ClotsBlood clots can form in the heart, legs, arteries, veins, bladder, urinary tract, and uterus. Risk factors include high blood pressure and cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and family history. Symptoms and treatment depend on the location of the clot.
 Can a Person Survive a Hemorrhagic Stroke?
Can a Person Survive a Hemorrhagic Stroke?A hemorrhagic stroke is a serious medical emergency and should be treated immediately. While survival rates are low, there are ways to improve your chances. Learn how to spot hemorrhagic symptoms, what causes them, and how they can be treated.
 Can a Sleep Study Detect Heart Problems?
Can a Sleep Study Detect Heart Problems?Sleep studies are used to identify sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, narcolepsy, and parasomnias. People with heart failure are more likely to experience central sleep apnea.
 Can DVT Cause Acute Limb Ischemia?
Can DVT Cause Acute Limb Ischemia?Acute limb ischemia caused by DVT is a rare and potentially fatal complication that can result in arterial circulation impairment, tissue ischemia, or limb gangrene.
 Can I Skip an Aspirin Dose?
Can I Skip an Aspirin Dose?For people prescribed aspirin for serious disease conditions, missing your doses could prove serious and, even, fatal, in some cases.
 Can You Drink Coffee While Taking Beta-Blockers?
Can You Drink Coffee While Taking Beta-Blockers?Since caffeine can reduce the efficacy of beta-blockers, it is advisable to avoid drinking excess coffee while taking these medications.
 Can You Reverse Plaque Buildup in Your Arteries?
Can You Reverse Plaque Buildup in Your Arteries?There are two types of cholesterol in your body. Doctors cannot remove plaque completely from your arteries, but treatments can reduce the size of a blockage.
 Can You Survive Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Can You Survive Deep Vein Thrombosis?Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is not a life-threatening condition if it is detected and treated in the early stages.
 Can You Tell if Your Heart Is Healthy?
Can You Tell if Your Heart Is Healthy?Your heart pumps blood throughout your body. You can tell if your heart is healthy by taking 10,000 steps per day and having good blood pressure, BMI, cholesterol and blood sugar numbers.
 Cardiomyopathy (Restrictive)
Cardiomyopathy (Restrictive)Restrictive cardiomyopathy, the rarest form of cardiomyopathy, is a condition in which the walls of the lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles) are abnormally rigid and lack the flexibility to expand as the ventricles fill with blood. The pumping or systolic function of the ventricle may be normal but the diastolic function (the ability of the heart to fill with blood) is abnormal. Therefore, it is harder for the ventricles to fill with blood, and with time, the heart loses the ability to pump blood properly, leading to heart failure.
 Causes of Chest Pain: Signs and Symptoms
Causes of Chest Pain: Signs and SymptomsChest pain may be caused by many conditions. Learn when chest discomfort, pressure, and tightness is a medical emergency. Find out the most likely causes of left-sided chest pain and chest pain when breathing. Read about potential underlying causes of chest pain including muscle pain, coronary artery disease, coronary artery dissection, esophageal conditions, gallbladder problems, GERD, heart attack, lung problems, and more. Discover how chest pain in women differs from that in men.
 Chest Pain
Chest PainChest pain is a common complaint by a patient in the ER. Causes of chest pain include broken or bruised ribs, pleurisy, pneumothorax, shingles, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, angina, heart attack, costochondritis, pericarditis, aorta or aortic dissection, and reflux esophagitis. Diagnosis and treatment of chest pain depends upon the cause and clinical presentation of the patient's chest pain.
 Claudication
ClaudicationClaudication is lower leg pain and/or cramping due to limited blood flow and lack of oxygen as a result of hardened or blocked arteries (atherosclerosis). Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is the most common cause. Learn more about other causes, symptoms, and how to treat claudication.
 Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)Congestive heart failure (CHF) refers to a condition in which the heart loses the ability to function properly. Heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, myocarditis, and cardiomyopathies are just a few potential causes of congestive heart failure. Symptoms of congestive heart failure may include fatigue, breathlessness, palpitations, angina, and edema.
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in the deep veins, and can be caused by broken bones, trauma to a limb, immobility, medications, smoking, cancer, genetic predisposition, and cancer. Symptoms and signs of a deep vein thrombosis in a leg are swelling, tenderness, redness, warmth, and pain. Treatments for DVT include medications and surgery.
 Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated CardiomyopathyDilated cardiomyopathy causes the heart muscles to progressively enlarge and weaken, reducing the ability of the heart to pump enough blood. Check out the center below for more medical references on heart disease, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related diseases, treatment, diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Does POTS Ever Go Away?
Does POTS Ever Go Away?Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) symptoms typically become more manageable over time, and, in some cases, symptoms may even disappear completely.
 Does Your Heart Rate Increase When Healing From Surgery?
Does Your Heart Rate Increase When Healing From Surgery?After surgery, your heart rate may increase. The condition is called postoperative tachycardia, in which heart rates are higher than 100 beats per minute.
- DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) During Pregnancy
Deep vein thrombosis or DVT is a condition in which a blood clot becomes embedded in one of the deep veins of the arms, thighs, pelvis, or lower legs. Warning signs and symptoms of DVT include pain, warmth, redness, swelling, leg cramps, and worsening leg pain in the affected extremity. Many conditions and other factors can cause DVTs, for example, during pregnancy including postpartum (6-8 weeks after delivery of the baby), obesity, heart attacks or heart failure, cancer, birth control pills (oral contraceptives), recent surgery, high altitudes, and advanced age. Treatment guidelines for DVT diagnosed during pregnancy is anticoagulation (anti-clotting) drugs, usually, low-molecular-weight heparins. DVT treatment may need to be continued postpartum. Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) should not be used to treat DVT during pregnancy because it can harm the developing fetus.
 DVT and Birth Control Pills
DVT and Birth Control PillsDeep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that has traveled deep into the veins of the arm, pelvis, or lower extremities. Oral contraceptives or birth control pills can slightly increase a woman's risk for developing blood clots, including DVT. DVT symptoms and signs in the leg include leg or calf pain, redness, swelling, warmth, or leg cramps, and skin discoloration. If a blood clot in the leg is not treated, it can travel to the lungs, which can cause a pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung) or post-thrombotic syndrome, both of which can be fatal if not treated immediately. Increased risk factors for DVT and birth control pills include over 40 years of age, family history, smoking, and obesity. Other medical problems that increase the risks of blood clots, for example, lung or heart disease, or inflammatory bowel disease or IBD (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC). Other options for preventing pregnancy include IUDs, birth control shots, condoms, diaphragms, and progestin-only oral contraceptives.
 Endocarditis
EndocarditisEndocarditis is a serious bacterial infection of one of the four heart valves. Endocarditis symptoms include fever, fatigue, weakness, chills, aching muscles and joints, night sweats, edema in the legs, feet, or abdomen, malaise, shortness of breath, and small skin lesions. Treatment for endocarditis usually involves antibiotics.
 Fainting (Syncope)
Fainting (Syncope)Fainting, passing out, blacking out, or syncope is the temporary loss of consciousness caused by a variety of situations such as vasovagal syncope, low blood pressure, and anemia. Learn about additional causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies.
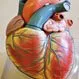 Heart Anatomy: Diagram, Blood Flow and Functions
Heart Anatomy: Diagram, Blood Flow and FunctionsThe heart is a very important organ in the body. It is responsible for continuously pumping oxygen and nutrient-rich blood throughout your body to sustain life. It is a fist-sized muscle that beats (expands and contracts) 100,000 times per day, pumping a total of five or six quarts of blood each minute, or about 2,000 gallons per day.
 Heart Attack
Heart AttackA heart attack (myocardial infarction) occurs when the sudden blockage of a coronary artery, usually because of blood clot, causes damage and death to heart muscle. Symptoms of a heart attack may include chest discomfort often described as a pain, pressure or tightness associated with shortness of breath, sweating and nausea.
 Heart Attack Prevention
Heart Attack PreventionThe process of developing hardening of the arteries begins in early childhood. This process puts a person at risk for heart attack and other coronary artery diseases. Once this process begins, it cannot be reversed. If you have diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart disease, you are at a higher risk of having a heart attack.
 Heart Attack vs. Heartburn
Heart Attack vs. HeartburnHeartburn is a symptom of another disease or medical problem and can be described as a feeling of burning in the chest accompanied by symptoms of nausea, vomiting, or a sour taste or food stuck in the back of the throat. Heart attack occurs when an artery in the heart is completely blocked by a blood clot, which causes that portion of heart muscle to die. Heart attack also has symptoms of chest pain, nausea, and vomiting, however, other warning signs and symptoms of a heart attack are unusual weakness or fatigue, and persistent and/or increased severity of symptoms over a few minutes. Heart attack is a life threatening emergency. If you think you or someone you are with is having a heart attack, call 911 immediately for urgent medical treatment. It may save your life.
 Heart Attack vs. Stroke
Heart Attack vs. StrokeA heart attack (myocardial infarction) happens when a clot completely blocks an artery supplying blood to the heart muscle, which results in heart muscle death. A stroke happens when part of the brain loses its blood supply (ischemic stroke) or there is bleeding within the brain (hemorrhagic stroke). Both heart attack and stroke can be fatal if not treated immediately.
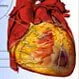 Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)Heart disease (coronary artery disease) occurs when plaque builds up in the coronary arteries, the vessels that supply blood to the heart. Heart disease can lead to heart attack. Treatment of heart disease involves control of heart disease risk factors through lifestyle changes, medications, and/or stenting or bypass surgery. Heart disease can be prevented by controlling heart disease risk factors.
 Heart Murmur
Heart MurmurA heart murmur is a heart problem that can occur, for example, during pregnancy or exercise, or it can be a symptom of a serious heart condition, for example, congenital heart defects or heart valve disease. A heart murmur makes a whooshing or swishing sound. Symptoms of a heart murmur include swelling of the legs or feet, dizziness or lightheadedness, blackouts, chest pain, rapid heart rate (palpitations), difficulty doing normal daily activities, fatigue, and a bluish tinge on the skin, lips, and fingernails. Treatment for heart murmurs in infants, children, and adults depends on the cause. Some heart murmurs can be harmless while some are serious and life-threatening.
 Heart Palpitations
Heart PalpitationsWhen you experience heart palpitations, you feel like your heart is racing or pounding. Anxiety, panic disorders, overeating, pregnancy, and abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can cause or trigger heart palpitations. Most palpitations are not serious, however, palpitations caused by a heart condition like atrial fibrillation can be serious and require medical treatment.
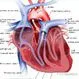 Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmias)
Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmias)Heart rhythm disorders (arrhythmias) occur when the heart's electrical system malfunctions. Discover the different types (like atrial fibrillation), causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and prevention tips.
 Hemophilia A and B
Hemophilia A and BHemophilia is defined as one of a group of inherited bleeding disorders. Hemophilia A and hemophilia B are inherited in an X-linked recessive genetic pattern. Symptoms of hemophilia include bleeding into the joints, muscles, GI or urinary tract, or brain or skull. Hemophilia treatment generally involves the replacement of blood clotting factors.
 High-Sensitivity Troponin Test
High-Sensitivity Troponin TestThe high-sensitive troponin test can detect very low levels of troponin T in the blood. (There are three types of cardiac troponin proteins, I, T, and C.), which helps doctors diagnose a heart attack more quickly. If troponin levels are elevated high and the ECG (EKG, electrocardiogram) indicates an acute heart attack, immediate cardiac intervention such as catheterization, stents, or a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG). The high-sensitive troponin test can help diagnose heart conditions such as obstructive coronary disease (CAD), stable angina, congestive heart failure, cardiomyopathy, chronic heart failure, myocarditis, aortic dissection, cardiotoxic chemotherapy, blunt trauma to the chest, and strenuous exercise, for example, endurance athletes. You can prevent elevated troponin levels in the blood with a heart-healthy lifestyle a heart-healthy diet, maintaining your weight, limit alcohol, don’t smoke, practice stress reduction through stress reduction techniques, meditation, and yoga, manage your blood pressure and diabetes, and take all of your medications as your doctor has instructed you. Call 911 immediately if you have chest pain and have symptoms of a heart attack, which include nausea, vomiting, belching, indigestion, upper abdominal discomfort that feels like stomach pain in the middle of the upper abdomen, upper back and arm pain, feeling as though you are getting the flu, sweating, a vague feeling of illness, and sweating.
 How Can I Bring My Blood Pressure Down Immediately?
How Can I Bring My Blood Pressure Down Immediately?High blood pressure is diagnosed when the force of your blood pressing against the artery wall is too high for an extended period of time. Bring your blood pressure down immediately by taking a hot shower or bath and practicing deep breathing and relaxation techniques.
 How Do You Fix Anemia?
How Do You Fix Anemia?Anemia describes a condition in which you have a low red blood cell count and low hemoglobin levels. This is a serious condition as red blood cells and hemoglobin carry oxygen to all your cells, allowing them to burn energy. If you're anemic, you'll likely feel fatigued and short of breath, lacking physical stamina. You may have heart problems and appear pale. Anemia is often a symptom of some other disease or condition, so treatment varies widely depending on the root cause.
 How Do You Fix May-Thurner Syndrome?
How Do You Fix May-Thurner Syndrome?May-Thurner syndrome occurs when the right iliac artery compresses the left iliac vein. Learn the causes, symptoms, risk factors, stages, diagnosis, and treatment of MTS.
 How Do You Get Rid of Swollen Feet and Ankles?
How Do You Get Rid of Swollen Feet and Ankles?Learn what medical treatments can help with swollen feet and ankles and speed up your recovery from swollen feet and ankles.
 How Do You Strengthen Your Heart After Heart Failure?
How Do You Strengthen Your Heart After Heart Failure?You can strengthen your heart after heart failure by making recommended changes to your diet, exercising regularly, and adopting healthy habits.
 How Does a Biventricular Pacemaker Work?
How Does a Biventricular Pacemaker Work?A biventricular pacemaker is a special type of pacemaker to treat heart failure with abnormal electrical systems. This type of pacemaker stimulates the lower left and right chamber of the heart.
 How Does Carotid Artery Disease Affect Your Daily Life?
How Does Carotid Artery Disease Affect Your Daily Life?The term carotid artery disease refers to the narrowing of the carotid arteries and can also be called carotid stenosis. Fatty substance buildup and cholesterol deposits, called plaque are the cause of the narrowing arteries. Carotid artery disease can be treated by following recommended lifestyle changes, taking prescription medications, and considering a procedure to improve blood flow, if your doctor believes it could help.
 How Is Porphyria Diagnosed?
How Is Porphyria Diagnosed?Porphyria, also known as “vampire disease,” is diagnosed through special tests, such as blood tests, fecal tests and urine tests, to look for excessive levels of porphyrin in the body.
- How Is Right Heart Catheterization Done?
Catheterization is the process where doctors use a thin, flexible tube called a catheter to look at the heart. Right heart catheterization is performed by going into a vein.
 How Long Can a Child Live With a Pacemaker?
How Long Can a Child Live With a Pacemaker?In most cases, most children can live a normal life after pacemaker surgery.
 How Long Can You Live With a Biventricular Pacemaker?
How Long Can You Live With a Biventricular Pacemaker?A biventricular pacemaker is a battery-operated device used to treat delay in contractions of the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). As per research, patients with a biventricular pacemaker have better survival rates after the diagnosis is made. The average life increases approximately between 8.5 and 20 years, depending on the overall health, age, and lifestyle.
 How Long Can You Live With Heart Failure?
How Long Can You Live With Heart Failure?What is the life expectancy of people with heart failure? Learn about survival rates, determining factors, and lifestyle changes that may help increase your life expectancy.
 How Long Can You Live With Heart Valve Disease?
How Long Can You Live With Heart Valve Disease?The heart has two upper (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). There are certain structures, called valves, present in the heart to regulate the flow of blood into, within, and out of the heart. These valves are flaps present at specific junctions in the heart.
 How Long Does an Electrophysiology Study Take?
How Long Does an Electrophysiology Study Take?An electrophysiology (EP) study is a test performed to determine the cause of abnormal heart rhythm and it usually takes about one to four hours to complete. However, it may take longer if additional treatments such as catheter ablation are performed at the same time by your heart surgeon.
 How Long Does SCAD Take to Heal?
How Long Does SCAD Take to Heal?Sudden coronary artery dissection (SCAD) may heal within a few weeks to several months.
 How Many Types of Cardiac Catheterization Are There?
How Many Types of Cardiac Catheterization Are There?During a heart catheterization, doctors insert the tube into a blood vessel. There are two types of cardiac catheterization, left and right heart catheterization.
 How Painful Is Bone Marrow Donor Procedure?
How Painful Is Bone Marrow Donor Procedure?The bone marrow donor procedure may involve some pain once the anesthesia wears off. Painkillers may be needed for the next few days.
 How Serious Is a Heart Catheterization?
How Serious Is a Heart Catheterization?Cardiac catheterization is a minimally invasive procedure that is considered to be safe for most patients. The procedure helps doctors find and fix any heart problems. It is a low-risk procedure and complications are usually rare, but as with any procedure, complications may arise.
 How Serious Is a Right Bundle Branch Block?
How Serious Is a Right Bundle Branch Block?For most people, a right bundle branch block (RBBB) is not a concern since it doesn’t result in symptoms and treatment is not required. However, in some cases, if RBBB develops after a heart attack it may indicate serious heart muscle damage.
 How Serious Is Aortobifemoral Bypass?
How Serious Is Aortobifemoral Bypass?An aortobifemoral bypass is a major surgery that has a success rate of about 80% and a mortality rate of about 2%-5%. Learn about associated risks and complications.
 How Serious Is Dilated Cardiomyopathy?
How Serious Is Dilated Cardiomyopathy?Dilated cardiomyopathy is a serious condition because it increases the chances of life-threatening conditions, such as heart failure, irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias), and blood clots. Dilated cardiomyopathy is the most common type of cardiomyopathy. In this condition, the walls of the heart become thin and the heart gets larger.
 How Serious Is Having a Stent Put In?
How Serious Is Having a Stent Put In?A stent is a tube that the surgeon fixes in a blocked artery. Most sites of stent placement are carotid arteries and coronary arteries.
 How Serious Is Left Bundle Branch Block?
How Serious Is Left Bundle Branch Block?Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is an abnormality in the heart’s electrical conduction system. Learn about symptoms and treatment.
 How Serious Is SVT?
How Serious Is SVT?Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is typically not serious unless you have an underlying heart condition. Learn about causes, symptoms, and when to call a doctor.
 How to Get Rid of Water Retention Fast
How to Get Rid of Water Retention FastWater retention or fluid retention can be caused due to several medical conditions and some medications. Edema is the medical term for swelling caused by the retention of excessive fluids in the body tissues.
 Hyperkalemia
HyperkalemiaHyperkalemia is an abnormally high level of potassium in the blood. Hyperkalemia symptoms include nausea, fatigue, tingling sensations, or muscle weakness. Hyperkalemia may also cause no symptoms. Hyperkalemia treatment may include a low-potassium diet, medications, and intravenous glucose and insulin. Causes of hyperkalemia include kidney dysfunction, certain medications, adrenal gland diseases, and potassium shifts.
 Hyponatremia (Low Blood Sodium)
Hyponatremia (Low Blood Sodium)Hyponatremia or low sodium levels in the blood can result in symptoms such as headache, confusion, seizures, weakness, restlessness, and muscle spasms. Kidney or congestive heart failure, hypothyroidism, cirrhosis, medications, or strenuous exercise without electrolyte replacement can cause hyponatremia. Treatment for hyponatremia are diet changes and electrolyte replacement with an IV.
 Is 120 Over 60 a Good Blood Pressure Reading?
Is 120 Over 60 a Good Blood Pressure Reading?If your systolic blood pressure is normal (between 100-120), and your diastolic blood pressure is lower (60 or below), you are considered to have low blood pressure, or isolated diastolic hypotension. Low diastolic blood pressure should be monitored closely.
 Is It Normal to Have Irregular Heartbeat After Ablation?
Is It Normal to Have Irregular Heartbeat After Ablation?Cardiac (heart) ablation is a procedure performed to correct heart arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythm/beat). Cardiac ablation works by intentionally injuring or destroying (ablating) and scarring the tissue in the heart that triggers the abnormal heart rhythm.
 Is Pacemaker Implantation a Major Surgery?
Is Pacemaker Implantation a Major Surgery?A pacemaker is a small, battery-operated device that sends signals to the heart to regulate the heartbeat. The pacemaker senses when the heart beats irregularly (arrhythmia) or if it beats too slow (bradycardia) and sends corrective signals to the heart muscles. Modern-day pacemakers can fix arrhythmias and help restore normal heart function.
 Is POTS a Serious Condition?
Is POTS a Serious Condition?Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a syndrome characterized by increased heart rate (tachycardia), a fall in blood pressure (hypotension) and giddiness when standing (orthostatic). In POTS, the symptoms occur because the heart does not receive sufficient blood supply when the person stands upright.
 Is Sinus Arrhythmia Serious?
Is Sinus Arrhythmia Serious?Sinus arrhythmia is a common, harmless condition that is not necessarily dangerous; however, it should be evaluated if accompanied by other signs of heart problems.
 Is SVT Life-Threatening?
Is SVT Life-Threatening?A person experiencing tachycardia has a resting heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute (bpm). Atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, and atrial flutter and atrial tachycardia and the three forms of supraventricular tachycardia.
 Life Expectancy of Someone With Marfan Syndrome
Life Expectancy of Someone With Marfan SyndromePeople who are accurately diagnosed, adapt proper lifestyles and receive appropriate medical and surgical management may live for a normal life span (into their 70s). However, there are no guarantees. Having Marfan syndrome does not mean patients might not acquire other conditions that are common in the aging population.
 Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral Valve ProlapseMitral valve prolapse is a common abnormality of the heart when the valve between the upper and lower left chambers doesn't close properly. Most people do show symptoms and do not require treatment. However, when symptoms do show, they include anxiety, sharp chest pain, palpitations, and migraines.
 Myelodysplastic or Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (Leukemia Types)
Myelodysplastic or Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (Leukemia Types)Myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative neoplasms are different types of blood disorders. Check out the center below for more medical references on blood disorders, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Myocarditis
MyocarditisMyocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle and can be caused by a variety of infections, conditions, and viruses. Symptoms of myocarditis include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid accumulation.
 Orthostatic Hypotension
Orthostatic HypotensionOrthostatic hypotension is a type of low blood pressure in which a person becomes dizzy, lightheaded, or faints when moving from a sitting position to a standing position. There are a variety of causes of this condition such as dehydration, medications, and diseases and conditions. Treatment depends on the cause of the condition.
 Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Paroxysmal Nocturnal HemoglobinuriaParoxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria or PNH is a rare genetic disease in which there is an abnormal breakdown of red blood cells. Symptoms of PHN include irregular heartbeats, chest pain, abdominal pain, anemia, jaundice, seizure, and blood clots in the legs (DVTs). Treatment for PNH is directed toward the symptoms of the disease.
 Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia
Paroxysmal Supraventricular TachycardiaParoxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT) is an abnormal conduction of electricity in particular areas of the heart. PSVT was referred to at one time as paroxysmal atrial tachycardia or PAT, however, the term PAT is reserved for as specific heart condition. Symptoms of PSVT include weakness, shortness of breath, chest pressure, lightheadedness, and palpitations. PSVT is treated with medications or procedures that return the heart to its normal electrical pattern.
 Pericarditis
PericarditisPericarditis is a heart condition in which the pericardium (the sac around your heart) is inflamed. The inflammation may produce a collection of fluid in the pericardial sac called pericardial effusion. Learn the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatments for pericarditis.
 Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) refers to diseases of the blood vessels (arteries and veins) located outside the heart and brain. Doctors commonly use the term peripheral vascular disease to refer to peripheral artery disease (peripheral arterial disease, PAD), a condition that develops when the arteries that supply blood to the internal organs, arms, and legs become completely or partially blocked as a result of atherosclerosis.
 Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious AnemiaPernicious anemia is a blood disorder in which the body does not make enough red blood cells due to a lack of vitamin B12 in the blood. Pernicious anemia can develop from a lack of a protein that helps the body absorb vitamin B12, not getting enough B12 in the diet, and certain intestinal conditions that interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12 such as Crohn's disease, celiac sprue, or ulcerative colitis. There is no cure for pernicious anemia, thus treatment is life-long.
 Phlebitis (Thrombophlebitis)
Phlebitis (Thrombophlebitis)Phlebitis is the inflammation of a vein. Thrombophlebitis is when a blood clot causes inflammation. Phlebitis can be superficial or deeper in the veins. A blood clot deep in a vein is deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Some of the common causes of phlebitis include prolonged inactivity, varicose veins, trauma to a vein, underlying cancers, clotting disorders, and other causes. Symptoms of phlebitis may be mild (pain, tenderness, redness, or bulging of a vein. Treatment of phlebitis depends on the cause.
 Platelet Disorder - Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP)
Platelet Disorder - Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP)Immune thrombocytopenia is a platelet disorder triggered in adults by infections. Check out the center below for more medical references on platelet disorders, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are premature, extra or irregular heartbeats that originate from the heart ventricles and disrupt heart rhythm. Explore causes such as heart attacks, high blood pressure, alcohol, and excess caffeine.
 Renal Artery Stenosis
Renal Artery StenosisRenal artery stenosis is a narrowing of the diameter of the renal arteries. When the renal arteries narrow, the result is restricted blood flow to the kidneys, which may lead to impaired kidney function and high blood pressure (referred to as renovascular hypertension (RVHT). Renal artery stenosis can occur in one or both kidneys. The primary cause of renal artery stenosis is atherosclerosis. Symptoms of renal artery stenosis include high blood pressure that does not respond to treatment and severe high blood pressure in individuals younger than 30 or greater than 50 years of age. Renal artery stenosis is diagnosed with imaging and functional tests. Treatment for renal artery stenosis includes medication or surgery.
 Should You Take CoQ10 Every Day?
Should You Take CoQ10 Every Day?CoQ10, short for coenzyme Q10, is a compound that’s naturally found in your body. CoQ10 is generally well-tolerated with very few side effects and is safe to take, but since lots of studies show that CoQ10 supplements might not have any benefit unless you have a health problem, it’s likely best to get it naturally from food.
 Side Effects of Having a Pacemaker
Side Effects of Having a PacemakerA pacemaker is a small device that sends electrical impulses to the heart muscles to maintain a suitable heart rate and rhythm. Pacemakers are used to treat an abnormal heart rate (arrhythmias).
 Spherocytosis (Hereditary, HS)
Spherocytosis (Hereditary, HS)Hereditary spherocytosis is a blood disorder that is inherited. In hereditary spherocytosis, the red blood cells are sphere-shaped instead of the normal shape of red blood cells, which is a concave disk shape. Signs and symptoms of hereditary spherocytosis include paleness, yellowing of the eyes and skin (jaundice), splenomegally, and gallbladder problems. Hereditary spherocytosis is treated with phototherapy, transfusions, and folic acid supplementation.
 Stroke Symptoms and Treatment
Stroke Symptoms and TreatmentA stroke is an interruption of the blood supply to part of the brain caused by either a blood clot (ischemic) or bleeding (hemorrhagic). Symptoms of a stroke may include weakness, numbness, double vision or vision loss, confusion, vertigo, difficulty speaking, or understanding speech. A physical exam, imaging tests, neurological exam, and blood tests may be used to diagnose a stroke.
 Stroke vs Aneurysm
Stroke vs AneurysmA stroke or "brain attack" is caused because blood flow to an area of the brain has been cut off by a blood clot or by a weakened or damaged blood vessel (for example, head trauma). The damaged area of the brain dies, which results in loss of function like speech capabilities, muscle movement, or muscles of an extremity like an arm or leg is reduced or lost completely. An aneurysm is a weakness in an artery wall. This weakness in the wall causes the artery to widen or balloon out, and then they rupture or break open.
 Sudden Cardiac Arrest
Sudden Cardiac ArrestSudden cardiac arrest is an unexpected, sudden death caused by sudden cardiac arrest (loss of heart function). Treatment of sudden cardiac arrest is an emergency, and action must be taken immediately.
 Survival Rate of Heart Valve Replacement Surgery
Survival Rate of Heart Valve Replacement SurgeryThe survival rate for a heart valve replacement surgery depends on which valve is involved. This was analyzed in a large study in which the lifespan of a large population, who went ahead with the surgery, is observed for a specific timeframe.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
 11 Heart-healthy Foods Good for Heart Patients
11 Heart-healthy Foods Good for Heart PatientsWhat to know about foods recommended for heart health. Learn about the key nutrients essential for heart health and which foods to add to your diet for a healthy heart.
 A Visual Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
A Visual Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a dangerous and sometimes fatal blood clot that occurs deep within the lower leg or thigh. Understand the symptoms, treatment and prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
 A Visual Guide to Vein and Artery Problems
A Visual Guide to Vein and Artery ProblemsSee pictures of vein and artery problems and learn about the causes and symptoms of conditions like coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease (PAD), varicose veins, and more from this WebMD slideshow.
 Am I Having a Heart Attack? Symptoms of Heart Disease
Am I Having a Heart Attack? Symptoms of Heart DiseaseHeart attacks symptoms vary greatly for men and women, from anxiety and fatigue to nausea and sweating. Learn the warning signs of a heart attack and know the symptoms that may require an immediate trip to the hospital.
 Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib) Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib) Quiz: Test Your Medical IQLearn the causes, symptoms, and treatments of the common heart abnormality known as atrial fibrillation (A-fib).
 Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Tips for Living with Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Tips for Living with Atrial FibrillationLearn how to live easier with atrial fibrillation. What is AFib? Find out the symptoms and causes of this heart condition. Explore tips that can help you manage an irregular heartbeat, including medication, diet, nutrition, exercise, and ways to reduce stress.
 Atrial Fibrillation: Foods to Watch When You Have AFib
Atrial Fibrillation: Foods to Watch When You Have AFibThink twice before you eat or drink these foods to help keep your heart healthy.
 Atrial Fibrillation: Heart Symptoms, Diagnosis, & AFib Treatment
Atrial Fibrillation: Heart Symptoms, Diagnosis, & AFib TreatmentAFib symptoms like heart racing, fluttering, and irregular heart beat may be caused by heart disease, obesity, alcohol use, thyroid disease, and other conditions. AFib medications may include blood thinners, drugs to control heart rate or convert the heart to a normal rhythm. AFib surgery is also a treatment possibility.
 Atrial Fibrillation: How to Treat Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial Fibrillation: How to Treat Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)Dealing with atrial fibrillation? WebMD shows you AFib treatments like ablation, cardioversion, pacemaker, and medicines including beta blockers and anticoagulants.
 Blood Clots: 4 Signs You Could Have One
Blood Clots: 4 Signs You Could Have OneBlood clots can be deadly medical emergencies that can form in different parts of your body. Learn the warning signs that you might have one.
 Blood Type: How Your Blood Type Can Affect Your Health
Blood Type: How Your Blood Type Can Affect Your HealthDoes your blood type play a role in your risk for disease? Find out how it fares in the face of certain conditions.
 Cardiac Arrest: What You Should Know
Cardiac Arrest: What You Should KnowCardiac arrest is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate medical care. Use this WebMD slideshow to know whether you are at risk for cardiac arrest and what you can do if it happens to a loved one.
 Cholesterol & Triglycerides: Mistakes That Can Affect Your Cholesterol
Cholesterol & Triglycerides: Mistakes That Can Affect Your CholesterolHigh cholesterol can be trouble. Find out from WebMD's slideshow if you’re doing things that can make it harder to keep your numbers in check.
 DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Quiz
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) QuizTake the Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Quiz to learn causes, symptoms, and treatments for these two dangerous conditions.
 DVT: 12 Tips to Improve Your Circulation
DVT: 12 Tips to Improve Your CirculationBlood needs to pump to every corner of your body to keep it running well. WebMD shows you how to rev up your circulation.
 DVT: Dos and Don’ts After a Blood Clot
DVT: Dos and Don’ts After a Blood ClotIf you’ve had a blood clot, like a deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE), you might need to make a few changes afterward to prevent another one. Here are some tips from WebMD you can use to stay healthy.
 Foot Health: Causes of Swollen Feet and Ankles
Foot Health: Causes of Swollen Feet and AnklesSwollen feet and ankles may be associated with conditions like pregnancy, injury, heart failure, kidney disease, liver disease, chronic venous insufficiency, and lymphedema. Treatment may include home remedies, exercise, magnesium, and certain medications.
 Guide to Blood Donation
Guide to Blood DonationInterested in giving blood? Your donation is needed more urgently than ever right now. Here’s what to know before you give.
 Heart Disease Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Heart Disease Quiz: Test Your Medical IQTake our Heart Disease Quiz to get answers and facts about high cholesterol, atherosclerosis prevention, and the causes, symptoms, treatments, testing, and procedures for medically broken hearts.
 Heart Disease: Alternative Treatments for AFib
Heart Disease: Alternative Treatments for AFibMedication and surgery aren't the only things that can improve or prevent your AFib symptoms. Talk to your doctor about these ideas from WebMD to help treat your condition.
 Heart Disease: Causes of a Heart Attack
Heart Disease: Causes of a Heart AttackHeart disease prevention includes controlling risk factors like diet, exercise, and stress. Heart disease symptoms in women may differ from men. Use a heart disease risk calculator to determine your heart attack risk.
 Heart Disease: How to Help Prevent an AFib Attack
Heart Disease: How to Help Prevent an AFib AttackThese simple things can make a flare-up of atrial fibrillation less likely.
 Heart Disease: Pill-Free Ways to Cut Your Heart Disease Risk
Heart Disease: Pill-Free Ways to Cut Your Heart Disease RiskYou don't have to take medicine to lower your heart disease risk. Find out more about how diet, exercise, and other lifestyle changes can help your heart.
 Heart Disease: Symptoms, Signs, and Causes
Heart Disease: Symptoms, Signs, and CausesWhat is heart disease (coronary artery disease)? Learn about the causes of heart disease, arrhythmias and myopathy. Symptoms of heart disease include chest pain and shortness of breath. Explore heart disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
 Heart Disease: Understand Your Blood and Urine Test Results
Heart Disease: Understand Your Blood and Urine Test ResultsYour blood and urine can reveal a lot about your health. Here's how to understand your lab test results.
 Heart Failure Quiz
Heart Failure QuizWhat is heart failure? Learn about this dangerous condition, as well as who is at risk, and what to do about it.
 Heart Health: What Is a Healthy and Normal Heart Rate for My Age?
Heart Health: What Is a Healthy and Normal Heart Rate for My Age?Learn normal heart rates by age, for young adults, seniors, and others. What's a good resting heart rate for your age? What is your target and maximum heart rate for men and women by age group? Learn these and more here.
 Heart Health: What to Know About Your Heart Rate
Heart Health: What to Know About Your Heart RateUnderstanding your heart rate and what's healthy for you is an important part of taking care of yourself. Get the facts about heart rates.
 Heart Palpitations: 14 Possible Causes and Should You Worry?
Heart Palpitations: 14 Possible Causes and Should You Worry?Heart palpitations are caused by stress, exercise, caffeine, nicotine, hormone changes, fever, medications, low blood sugar, overactive thyroid, heart rhythm problems, alcohol, PVCs, and illegal drugs. Doctors may use tests like an ECG, Holter monitor, event monitor, and electrocardiogram to help diagnose the underlying cause of heart palpitations.
 How Can I Lower My Blood Pressure Immediately, Naturally? Chart
How Can I Lower My Blood Pressure Immediately, Naturally? ChartCan you lower your high blood pressure immediately? Explore 9 ways such as exercise, healthy eating, rest, and more that can help protect your arteries from blood pressure changes as you age. See chart and learn to manage and control hypertension the healthy and natural way.
 Hypertension: What High Blood Pressure Can Do to Your Body
Hypertension: What High Blood Pressure Can Do to Your BodyHigh blood pressure puts you at risk for a number of other conditions. Here's what to look out for.
 Omega 3 Foods: Health Benefits, Research, Best Supplements
Omega 3 Foods: Health Benefits, Research, Best SupplementsWhat does research say are the best omega 3 supplements? What are the benefits of omega 3 fatty acids? Learn how Omega 3 rich foods like fish oil, salmon, walnuts, & more can boost brain power, save you from joint pain, ease depression and create a healthier you.
 Picture of Aorta
Picture of AortaThe aorta is the largest artery in the body. See a picture of the Aorta and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Balloon Angioplasty
Picture of Balloon AngioplastyCoronary angioplasty is accomplished using a balloon-tipped catheter inserted through an artery in the groin or arm to enlarge a narrowing in a coronary artery. See a picture of Balloon Angioplasty and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Blood Clot
Picture of Blood ClotBlood that has been converted from a liquid to a solid state. See a picture of Blood Clot and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Heart
Picture of HeartThe muscle that pumps blood received from veins into arteries throughout the body. See a picture of the Heart and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Heart Catheter
Picture of Heart CatheterCatheter procedures are much easier than surgery on patients because they involve only a needle puncture in the skin where the catheter is inserted into a vein or an artery. See a picture of Heart Catheter and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Heart Detail
Picture of Heart DetailThe heart is composed of specialized cardiac muscle, and it is four-chambered, with a right atrium and ventricle, and an anatomically separate left atrium and ventricle. See a picture of Heart Detail and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Pericardial Sac
Picture of Pericardial SacA conical sac of fibrous tissue which surrounds the heart and the roots of the great blood vessels. See a picture of Pericardial Sac and learn more about the health topic.
 Picture of Pitting Edema
Picture of Pitting EdemaObservable swelling of body tissues due to fluid accumulation that may be demonstrated by applying pressure to the swollen area (such as by depressing the skin with a finger). See a picture of Pitting Edema and learn more about the health topic.
 Stroke Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Stroke Quiz: Test Your Medical IQTake the Stroke Quiz to learn about stroke risks, causes, treatment, and most importantly, prevention.
 Sudden Cardiac Arrest - Test Your Heart Health IQ
Sudden Cardiac Arrest - Test Your Heart Health IQTake the Sudden Cardiac Arrest Quiz. Learning about this potentially deadly condition may save a life.
 Surprising Causes of DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis)
Surprising Causes of DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis)Long flights aren't the only thing that put you at risk for deep vein thrombosis. WebMD tells you about the lesser-known causes of potentially life-threatening blood clots.
 Ten Things That Put Athletes at Risk for DVT
Ten Things That Put Athletes at Risk for DVTDiscover the connection between athletes and deep vein thrombosis. Learn what puts athletes at risk for developing DVT.
 What Are Normal Blood Pressure Ranges by Age For Men and Women?
What Are Normal Blood Pressure Ranges by Age For Men and Women?What is normal, low and high blood pressure? Find charts of blood pressure readings and ranges for men and women of different ages. Discover what causes high and low blood pressure and how to prevent it.
 What Happens After a Stroke? Signs, Symptoms, Types
What Happens After a Stroke? Signs, Symptoms, TypesWhat is a stroke? Learn about the different types of stroke, as well as many symptoms like sudden numbness or weakness, confusion, vision problems, or problems with coordination. Discover causes and recovery of a stroke.
Treatment & Diagnosis
- Apheresis (Hemapheresis, Pheresis)
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Test
- Can Atrial Fibrillation Go Away?
- Chest X-Ray
- Complete Blood Count
- Coronary Angioplasty
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
- Coronary Brachytherapy
- CT Coronary Angiogram
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
- Ferritin Blood Test
- Heart Transplant
- Heart Valve Disease Surgery
- Hemoglobin
- Homocysteine Blood Test
- How Dangerous Is Percutaneous Heart Valve Replacement Surgery?
- How Is A Sternotomy Done?
- How Is Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Done?
- How Is PDA Surgery Performed?
- How Long Can You Live After a Heart Transplant?
- How Long Do Carotid Artery Stents Last?
- How Long Does a Mitral Valvuloplasty Last?
- How Long Does It Take for Angio-Seal to Dissolve?
- How Long Does It Take to Recover From Heart Ablation Surgery?
- How Serious Is a Heart Ablation Surgery?
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
- Is Pericardial Window Surgery Dangerous?
- Is Radial Pulse Accurate?
- Is the External Jugular Vein a Central Line or a Peripheral Line?
- Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD)
- Myocardial Biopsy
- Tilt Table Test
- Transmyocardial Laser Revascularization (TMR)
- What Are the Antibiotic Prophylactic Regimens for Endocarditis?
- What Are The Four Heart Sounds?
- What Are the Indications for Transcutaneous Cardiac Pacing?
- What Are the Side Effects of Embolization?
- What Are Three Signs of Cardiac Tamponade?
- What Does a Cardiologist Do?
- What Does an Echocardiogram Test For?
- What Foods Trigger Atrial Fibrillation?
- What Is a Percutaneous Valve Replacement Procedure?
- What Is a Permanent Pacemaker?
- What Is a Pharmacologic Stress Testing Used For?
- What Is a Transradial Heart Catheterization Procedure?
- What Is a Venous Cutdown Procedure?
- What Is DDDR Pacing?
- What Is PDA Heart Surgery?
- What Is Pericardiocentesis?
- What Is the Best Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation?
- What Is the Difference Between Electrocardiogram and Electrocardiograph?
- Where Is an Arterial Line Placed?
Medications & Supplements
- Activase (alteplase) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- adenosine
- Aldactone (spironolactone)
- Aldactone (spironolactone) Side Effects, Interactions, and Warnings
- alteplase (TPA, Activase, Cathflo Activase)
- amiodarone, Cordarone, Nextrone, Pacerone
- amlodipine besylate
- Anticoagulants
- atenolol
- atenolol - oral, Tenormin
- atropine/pralidoxime
- benazepril (Lotensin HTC)
- bepridil (Vascor)
- Beta Blockers
- BETA BLOCKERS-ORAL
- Betapace (sotalol)
- bezafibrate
- BiDil (isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine HCI)
- Brevibloc (esmolol hydrochloride) Injection
- Camzyos (mavacamten)
- cangrelor (Kengreal)
- Cardiogen-82 (rubidium Rb 82 generator)
- Carospir (spironolactone)
- carvedilol
- cilostazol (Pletal)
- clopidogrel bisulfate (Plavix)
- coenzyme Q10
- dabigatran (Pradaxa)
- dalteparin injection (Fragmin)
- Definity (perflutren lipid microsphere)
- Diamox (acetazolamide)
- Digitek (digoxin)
- digoxin (Lanoxin, Lanoxin Pediatric)
- diltiazem (Cardizem, Cardizem CD, Cardizem LA, Tiazac, Cartia XT, Diltzac, Dilt-CD, and several oth)
- Diovan HCT (valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- dobutamine
- dopamine
- dopamine
- edoxaban
- Effient (prasugrel)
- Eliquis (apixaban)
- enoxaparin
- Entresto (sacubitril and valsartan)
- Entresto (sacubitril and valsartan)
- eplerenone
- evening primrose oil
- Ezallor (rosuvastatin)
- flecainide
- fosinopril sodium, Monopril
- guanabenz
- hawthorn
- heparin
- heparin (Hemochron, Hep-Lock)
- Ibuprofen and Plavix
- idarucizumab
- Integrilin (eptifibatide)
- isosorbide dinitrate (Isordil Titradose)
- isosorbide mononitrate (Imdur, Ismo, Monoket)
- lily of the valley
- lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil, Qbrelis) ACE Inhibitor
- Lumason (sulfur hexafluoride lipid-type A microspheres)
- magnesium sulfate (antidote)
- metoprolol
- midodrine (Orvaten, ProAmatine)
- Multaq (dronedarone)
- mycophenolate mofetil (CellCept)
- nadolol (Corgard)
- nifedipine (Procardia, Adalat, Afeditab)
- Nikita (pitavastatin)
- Nitrates (Medication)
- nitroglycerin IV
- nitroglycerin sublingual
- nitroglycerin, Nitro-Bid, Nitro-Dur, Nitrostat, Transderm-Nitro, Minitran, Deponit, Nitrol
- norepinephrine
- omega 3 fatty acids
- omega-3-acid ethyl esters (Lovaza)
- Optiray (ioversol)
- pentoxifylline (Trental, Pentoxil)
- phenylephrine
- potassium chloride; K-Dur, KLor Con, K-Tab, Kaon CL, Klorvess, Slow-K, Ten-K, Klotrix, K-Lyte CL
- prasugrel
- prazosin
- procainamide, Pronestyl; Procan-SR; Procanbid (These brands no longer are available in the U.S.)
- propafenone (Rythmol)
- propranolol
- quinapril (Accupril)
- quinidine (Discontinued Brands: Cardioquine, Cin-Quin, Duraquin, Quinidex, Quinora, Quinact)
- ramipril
- ranolazine
- resveratrol
- rivaroxaban
- Side Effects of Brilinta (ticagrelor)
- Side Effects of Bumex (bumetanide)
- Side Effects of Calan (verapamil)
- Side Effects of Cardene (nicardipine)
- Side Effects of Cordarone (amiodarone)
- Side Effects of Corgard (nadolol)
- Side Effects of Corlanor (ivabradine)
- Side Effects of Crestor (rosuvastatin)
- Side Effects of Demadex (torsemide)
Prevention & Wellness
- Can You Drink Alcohol With Heart Failure?
- How Can I Improve My HRV?
- How Do You Fix Low Iron Deficiency?
- How Do You Know If You Lack Iron?
- Is a Diastolic of 50 Too Low?
- Is Donating Plasma Good for Your Body?
- What Are the Major Arteries?
- What Are the Symptoms of Low Iron Deficiency?
- What Causes a Person to Have Low Iron?
- What Does Nitric Oxide Do to Your Body?
- What Happens When Your Iron Is Low?
- What Heart Rate Is Too High?
- What Is a Good Heart Rate for My Age Chart?
- What Is Heart Rate Variability (HRV)?
- What Is the Main Function of Cytoplasm in a Cell?