Trending Diabetes Topics
Diabetes (Type 1 and Type 2)
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood. The two types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. Symptoms of diabetes include increased urine output, thirst, hunger, and fatigue. Treatment of diabetes depends on the type.
Type 2 Diabetes Pictures Slideshow
Watch this slideshow to understand type 2 diabetes and learn the warning signs. You'll see a pictorial overview of the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Quiz
Take the Diabetes Quiz and learn the causes, signs, symptoms, and types of this growing epidemic. What does diabetes have to do with obesity and diet? Learn about life as a diabetic.
Hypoglycemia
Learn about hypoglycemia, which is caused by low blood sugar. The symptoms of hypoglycemia may include anxiety, sweating, tremor, palpitations, nausea, and weakness. Consuming lifesavers, table sugar, soda, and juice are good treatment options.
Diabetes Foot Problems
For people with diabetes, too much glucose in the blood can cause serious foot complications such as nerve damage, infection, ulcers and even amputation. Watch this slideshow on diabetes related foot problems and help prevent serious complications.
Celebrities & Diabetes
Watch this slideshow of pictures of celebrities with type 1 or type 2 diabetes including Halle Berry, Salma Hayek, and Nick Jonas from The Jonas Brothers.
Related Disease Conditions
 Are Bananas Good for Diabetes?
Are Bananas Good for Diabetes?Bananas are a type of fruit that is rich in nutrients. People who have diabetes can consume bananas in moderation, preferably if they are small, unripe, and eaten along with protein and healthy fats.
 Can a Fit Person Get Diabetes?
Can a Fit Person Get Diabetes?No matter how thin or fit you are, you can still get diabetes. About 10%-15% of people with type II diabetes are at a healthy weight, a condition called lean diabetes.
 Can Diabetes Make My Legs Hurt?
Can Diabetes Make My Legs Hurt?Diabetes is a major cause of pain and uncomfortable sensations in the legs. Diabetic leg pain may present as a dull ache in the soles, calves, and thighs or as pins and needles in the lower limbs.
 Can You Survive Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Can You Survive Diabetic Ketoacidosis?Because it typically takes hours for DKA to become life-threatening, you can survive the condition by acting quickly and receiving timely medical treatment.
 Diabetes Foot Problems
Diabetes Foot ProblemsDiabetes foot problems can be progressive and initially may be considered minor. The patient may complain of changes to the skin and toenails like dryness, blisters, or sores. Small cuts or skin abrasions may not heal and can become infected. Prevention is key to diabetic foot care and it begins when diabetes is first diagnosed.
 Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1 and Type 2)
Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1 and Type 2)Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. The two types of diabetes are referred to as type 1 (insulin dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin dependent). Symptoms of diabetes include increased urine output, thirst, hunger, and fatigue.
 Diabetes Treatment
Diabetes TreatmentThe major goal in treating diabetes is controlling elevated blood sugar without causing abnormally low levels of blood sugar. Type 1 diabetes is treated with insulin, exercise, and a diabetic diet. Type 2 diabetes is first treated with weight reduction, a diabetic diet, and exercise. When these measures fail to control the elevated blood sugar, oral medications are used. If oral medications are still insufficient, insulin medications are considered.
 Diabetic Diet
Diabetic DietA diabetic diet focuses on balanced meals with controlled portions that get digested into the body in a slow, controlled way, so that blood sugar levels don’t spike after eating. It is composed of whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. It also limits processed foods, sugary drinks, and refined carbohydrates. The goal of the diet is to manage blood sugar levels in the blood and to maintain a healthy weight.
 Diabetic Home Care and Monitoring
Diabetic Home Care and MonitoringManaging your diabetes is a full time commitment. The goal of diabetic therapy is to control blood glucose levels and prevent the complications of diabetes. Information about exercise, diet, and medication will help you manage your diabetes better. Blood glucose reagent strips, blood glucose meters, urine glucose tests, tests for urinary ketones, continuous glucose sensors, and Hemoglobin A1C testing information will enable you to mange your diabetes at home successfully.
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Diabetic KetoacidosisDiabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a complication of type 1 diabetes that is life threatening. If a person thinks they may have diabetic ketoacidosis they should seek medical care immediately. Diabetic ketoacidosis happens when a person's insulin levels in the blood become dangerously low. Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis include dehydration, abdominal pain, confusion, and nausea and vomiting. Diabetic ketoacidosis needs medical treatment. It cannot be treated at home.
 Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic NeuropathyDiabetic neuropathy is a condition in which nerve damage has occurred as a complication of diabetes. The pain from the nerve damage can be severe with tingling or numbness in the part of the body affected. Diabetic neuropathy can occur anywhere in the body. Diabetic neuropathy can cause symptoms like intense pain, numbness, burning, or tingling in the part of the body affected by the condition. There are four types of neuropathy, which include peripheral, autonomic, proximal, and focal. Natural therapies and medications may help relieve the pain and other symptoms of diabetic neuropathy.
 Early Signs of Diabetes in Women: Symptoms and What to Watch For
Early Signs of Diabetes in Women: Symptoms and What to Watch ForDiabetes symptoms in women include vaginal itching, pain, or discharge, loss of interest or pain after having sex, polycystic ovarian syndrome (POS), and urinary tract infections or UTIs.
 Eye Problems and Diabetes
Eye Problems and DiabetesDiabetes and eye problems are generally caused by high blood sugar levels over an extended period of time. Types of eye problems in a person with diabetes include glaucoma, cataracts, and retinopathy. Examples of symptoms include blurred vision, headaches, eye aches, pain, halos around lights, loss of vision, watering eyes. Treatment for eye problems in people with diabetes depend on the type of eye problem. Prevention of eye problems include reducing blood pressure, cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, and maintaining proper blood glucose levels.
 How Do People With Diabetes Heal Sores?
How Do People With Diabetes Heal Sores?If you have diabetes, you are more likely to develop ulcers that do not heal as quickly as they should. People with diabetes can heal sores with proper wound care and medical treatment.
 How Do You Bring Blood Sugar Down Quickly?
How Do You Bring Blood Sugar Down Quickly?The medical term for high blood sugar is hyperglycemia. If you have diabetes, exercise, extra fluids, and insulin are easy ways to lower blood sugar levels naturally.
 How Long Does It Take to Reverse Prediabetes?
How Long Does It Take to Reverse Prediabetes?It can take anywhere from weeks to months to even a few years to reverse prediabetes. Learn about how you can reverse prediabetes through diet, weight loss, and exercise. Check out the center below for more medical references on diabetes, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related diseases, treatment, diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 How Many Units of Insulin Do I Need for 400 Blood Sugar?
How Many Units of Insulin Do I Need for 400 Blood Sugar?Theoretically, to reduce 400 mg/dL blood sugar to about 100 mg/dL, you would need at least 10 units of insulin. However, this depends on your weight and other factors.
 How to Prevent Diabetes Naturally
How to Prevent Diabetes NaturallyType 2 diabetes can be prevented naturally with a healthy lifestyle, for example, a Mediterranean diet, getting more exercise, quitting smoking, reducing stress, and in some cases, a combination of lifestyle changes and medication.
 Hyperglycemia
HyperglycemiaHyperglycemia or high blood sugar is a serious health problem for diabetics. There are two types of hyperglycemia, fasting and postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia can also lead to ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS). There are a variety of causes of hyperglycemia in people with diabetes. Symptoms of high blood sugar may include increased thirst, headaches, blurred vision, and frequent urination. Treatment can be achieved through lifestyle changes or medication changes. Carefully monitoring blood glucose levels is key to prevention.
 Hypoglycemia
HypoglycemiaLow blood sugar or hypoglycemia occurs when blood sugar is dangerously low and is often complication of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Learn about symptoms, dangers, and treatment.
 Hypoglycemia Without Diabetes: Causes and Diet
Hypoglycemia Without Diabetes: Causes and DietHypoglycemia (low blood sugar level) is a condition most seen in patients with diabetes, who are on insulin or medications. Hypoglycemia is uncommon to happen in people without diabetes.
 Insulin Resistance
Insulin ResistanceInsulin resistance is the diminished ability of cells to respond to the action of insulin in transporting glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream into muscle and other tissues. Some of the risk factors for insulin resistance include fatty liver, heart disease, strokes, peripheral vascular disease, high cholesterol, and smoking.
 Is a Glucose Level of 101 Bad?
Is a Glucose Level of 101 Bad?It means that you should control your blood sugar level through your diet. Otherwise, you may develop diabetes. This is a warning sign that you should stop ingesting extra glucose through your diet.
 Is Diabetes Inherited From Mother or Father?
Is Diabetes Inherited From Mother or Father?Diabetes is a hereditary disease, which means that the child is at high risk of developing diabetes compared to the general population at the given age. Diabetes can be inherited from either mother or father.
 Is There a Cure for Neuropathy in the Legs?
Is There a Cure for Neuropathy in the Legs?There is no cure for peripheral neuropathy. Some cases may improve with rigorous blood sugar control and insulin or with dialysis or renal transplantation.
 Lipodystrophy
LipodystrophyLipodystrophy is a syndrome in which body fat tissue is lost or abnormally accumulated in the whole body or just areas of it. Three forms of this disease are genetic (familial), acquired due to previous infections or HIV treatment), and congenital (present at birth). Diabetics often get it if they inject insulin in the same spot over a period of time.
 Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic SyndromeThe main features of metabolic syndrome include insulin resistance, hypertension (high blood pressure), cholesterol abnormalities, and an increased risk for clotting. Patients are most often overweight or obese. Lifestyle modification such as the Mediterranean diet, exercise, and quitting smoking are the preferred treatment of metabolic syndrome.
 Normal Blood Sugar Levels in Adults with Diabetes
Normal Blood Sugar Levels in Adults with DiabetesPeople with diabetes can manage and prevent low or high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia) by keeping a log of their blood sugar levels when they are eating and fasting and eating foods that are high in carbohydrates and sugar, for example, buttered potatoes, candy, sugary desserts, and fatty foods. Blood tests, for example, the hemoglobin A1c test (A1c test) and urinalysis can diagnose the type of diabetes the person has. Diabetes during pregnancy, called gestational diabetes, should be managed by you and your OB/GYN or another healthcare professional. Extremely high levels of blood glucose in the blood can be dangerous and life-threatening if you have type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes.
 Prediabetes
PrediabetesPrediabetes is a condition in which a person's blood sugar is higher than it should be, but it's not high enough to be full-blown diabetes. Learn the causes, symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, diet, and prognosis of prediabetes.
 Safe Cold Flu Drugs With Diabetes
Safe Cold Flu Drugs With DiabetesIf you have diabetes and catch a cold or the flu, it can be more difficult to recover from infections and their complications, for example, pneumonia. Home remedies and over-the-counter (OTC) drugs used for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of colds and the flu may affect blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. If you have diabetes and are sick with a cold or flu, you need to check your blood sugar levels more frequently.
 semaglutide
semaglutideSemaglutide is a medication used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and for chronic weight management, along with physical exercise, dietary restrictions, and lifestyle changes. Semaglutide is used to control blood sugar levels when other commonly prescribed medications do not control the sugar levels adequately in type 2 diabetes, but cannot be used to treat type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis, a complication of diabetes. Common side effects of semaglutide include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, indigestion (dyspepsia), abdominal distension, decrease in appetite, belching (eructation), gas (flatulence), gastritis, gastroenteritis, viral gastroenteritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gallstones (cholelithiasis), headache, fatigue, dizziness, low blood glucose level (hypoglycemia), severe hypoglycemia, diabetic retinopathy, and others. Do not take if breastfeeding.
 Signs of Diabetes in Men
Signs of Diabetes in MenEarly symptoms of diabetes are different in men, such as low testosterone. In many cases, prediabetes that will progress to type 2 diabetes if it is not treated early.
 Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 DiabetesType 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to a lifelong inability to produce insulin and requiring daily insulin replacement.
 Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes: Similarities and Differences
Type 1 vs. Type 2 Diabetes: Similarities and DifferencesDiabetes is a metabolic disease that involves a problem with the way insulin is processed in the body. People with type 1 diabetes usually are diagnosed during childhood and have a problem with insulin production by the pancreas. On the other hand, type 2 usually is caused by poor diet, lack of exercise and activity, or being overweight. However, there are genetic causes for both of these types of diabetes.
 Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 DiabetesType 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that may be reversible with diet and lifestyle changes. Symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, weight loss, fatigue, and an unusual odor to your urine. Most people don't know they have type 2 diabetes until they have a routine blood test. Treatment options include medications, a type 2 diabetes diet, and other lifestyle changes.
 Type 2 Diabetes Diet Plan
Type 2 Diabetes Diet PlanA type 2 diabetes diet or a type 2 diabetic diet is important for blood sugar (glucose) control in people with diabetes to prevent complications of diabetes. There are a variety of type 2 diabetes diet eating plans such as the Mediterranean diet, Paleo diet, ADA Diabetes Diet, and vegetarian diets. Learn about low and high-glycemic index foods, what foods to eat, and what foods to avoid if you have type 2 diabetes.
 Types of Diabetes Type 2 Medications
Types of Diabetes Type 2 MedicationsConsumer information about the types of type 2 diabetes medications. Read about the side effects of Precose, Diabinese, Amaryl, Glucophage, Actos, Avandia, Starlix, Prandin, and more. Drug interactions, dosing, storage, and breastfeeding and pregnancy safety information is provided.
 What Are the Early Signs of Diabetes?
What Are the Early Signs of Diabetes?The early signs of diabetes depend on if one has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes usually occurs in children, whereas type 2 diabetes is prevalent in adults.
 What Are the First Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?
What Are the First Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia?Hypoglycemia is an abnormally low blood sugar level. It is most common in patients with diabetes mellitus who are taking insulin and skip their meals. Patients with hypoglycemia should learn to recognize early symptoms to avoid serious complications.
 What Country Has the Most Type 1 Diabetes?
What Country Has the Most Type 1 Diabetes?According to research, type 1 diabetes is most common among non-Hispanic Caucasians, followed by African Americans and Hispanic Americans.
 What Does a 71-Blood Sugar Mean?
What Does a 71-Blood Sugar Mean?While a blood sugar level of 71 mg/dL is considered normal, levels below 70 mg/dL are considered low. Check out the center below for more medical references on blood sugar levels, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 What Does High Ketones in Blood Mean?
What Does High Ketones in Blood Mean?If you have diabetes, high ketone levels in your blood or urine could mean that you have diabetic ketoacidosis, which can be life-threatening. But healthy people on a keto diet may also have high ketone levels, but without any significant problems.
 What Does Ozempic Do to Your Body?
What Does Ozempic Do to Your Body?Ozempic is a medication for people with type II diabetes that helps stimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas. Check out the center below for more medical references on type II diabetes, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 What Foods Will Lower Blood Sugar Quickly?
What Foods Will Lower Blood Sugar Quickly?Diabetes or diabetes mellitus is a long-term health condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels. While there are no foods that bring down blood sugar levels quickly, adding the following to your diet can help keep your diabetes under control.
 What Fruits Should Diabetics Avoid?
What Fruits Should Diabetics Avoid?Managing diabetes successfully is about managing a combination of blood glucose levels. Diabetics do not have to avoid fruit, but they should adhere to sensible portion sizes and watch their overall carb intake.
 What is a High Insulin Level?
What is a High Insulin Level?Insulin is a hormone that is secreted by an abdominal organ called the pancreas. High insulin levels are levels of the hormone that are higher than they should be after ingesting glucose.
 What Is a Normal Blood Sugar Level by Age?
What Is a Normal Blood Sugar Level by Age?Normal blood sugar levels in adults and children vary from 90 to 180 mg/dL. Check out the center below for more medical references on blood sugar, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 What Is Actrapid Insulin?
What Is Actrapid Insulin?Actrapid contains human insulin which is used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Check out the center below for more medical references on diabetes, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 What Is Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)?
What Is Diabetic Macular Edema (DME)?Diabetic macular edema (DME) is an ocular complication of diabetes that develops over a period of time.
 What is the Best Herb for Lowering Blood Sugar?
What is the Best Herb for Lowering Blood Sugar?Many herbs have been studied for their medicinal properties. Most studies show that the best herb for diabetes is barberry.
 What Is the Survival Rate of Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
What Is the Survival Rate of Diabetic Ketoacidosis?With appropriate and timely treatment, the survival rate of DKA is quite high at over 95%. Survival rates are poorer in the elderly and those with known organ damage.
 What Percentage of Japanese Have Diabetes?
What Percentage of Japanese Have Diabetes?The prevalence of diabetes has been on the rise in Japan in recent years. The increase can be ascribed to a sedentary lifestyle and increased fat consumption.
 What Should I Do If I Have Ketones in My Urine?
What Should I Do If I Have Ketones in My Urine?If your urine reports show moderate or high levels of ketones, consult your doctor right away.
 What Should I Eat the Day Before My 3-Hour Glucose Test?
What Should I Eat the Day Before My 3-Hour Glucose Test?For three days before your glucose test, you can consume about 150 grams or 10 servings of carbohydrates.
 What Triggers Reactive Hypoglycemia?
What Triggers Reactive Hypoglycemia?Triggers for reactive hypoglycemia include alcohol, sugar, simple carbohydrates, and bakery goods. Check out the center below for more medical references on low blood sugar, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 What Types of Insulin Are Used for Sliding Scale Therapy?
What Types of Insulin Are Used for Sliding Scale Therapy?The types of insulin used for sliding scale therapy include long-acting insulin, short-acting insulin, and premixed insulin.
 Which Foods Should You Avoid If You Have Hypoglycemia?
Which Foods Should You Avoid If You Have Hypoglycemia?People suffering from hypoglycemia should avoid certain foods, such as trans and saturated fats, sugar-rich foods, processed foods, excessive caffeine, and alcohol.
 Which is Worse, Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes?
Which is Worse, Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes?Learn about the similarities and differences between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes.
 Why Can't People With Diabetes Go in Hot Tubs?
Why Can't People With Diabetes Go in Hot Tubs?Hot tubs pose health risks to people with diabetes due to peripheral neuropathy, slow wound healing, and the danger of overheating. Here are precautions to take before going in a hot tub.
 Why Do I Feel So Sick on Ozempic?
Why Do I Feel So Sick on Ozempic?Ozempic is a diabetes medication that slows down stomach emptying, which may cause mild to moderate stomach upset and nausea. Check out the center below for more medical references on diabetes medications, including multimedia (slideshows, images, and quizzes), related disease conditions, treatment and diagnosis, medications, and prevention or wellness.
 Why Does My Blood Sugar Fluctuate So Much?
Why Does My Blood Sugar Fluctuate So Much?Even if you keep an eye on what you eat and take medications as prescribed, you will likely see your blood sugar fluctuate due to some factors beyond your control.
 Will Drinking Water Lower Blood Sugar?
Will Drinking Water Lower Blood Sugar?Diabetes mellitus is a chronic health condition that affects your body's ability to break down food into energy. One study suggests that routinely drinking water might prevent the onset of hyperglycemia.
Multimedia: Slideshows, Images & Quizzes
 10 Muscle-Building Exercises for Diabetes
10 Muscle-Building Exercises for DiabetesWatch this slideshow on Diabetes and Exercise. If you have diabetes, see how strengthening your muscles with these 10 weight training exercise moves can help control your blood sugar.
 Diabetes Diet: 11 Low-Sugar Drink Ideas
Diabetes Diet: 11 Low-Sugar Drink IdeasSearching for low-sugar drink ideas? This pictures slideshow has eleven beverages ideal for people with diabetes and those looking to cut down on sugary drinks. Learn to make diet lemonades, fruit smoothies, ginger ale, cafe mochas and more.
 Diabetes Diet: Healthy Meal Plans for Diabetes-Friendly Eating
Diabetes Diet: Healthy Meal Plans for Diabetes-Friendly EatingDiscover the best and worst meals for diabetes-savvy dining. See how to avoid carbs and control your blood sugar with healthier meal combinations that retain all the foods and flavors you love.
 Diabetes Nerve Pain: Improving Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetes Nerve Pain: Improving Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyLearn how to cope with the symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy through pain management exercises. Find relief for diabetic nerve pain without medication.
 Diabetes Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Diabetes Quiz: Test Your Medical IQTake the Diabetes Quiz and learn the causes, signs, symptoms, and types of this growing epidemic. What does diabetes have to do with obesity and diet? Learn about life as a diabetic.
 Diabetes Tips: Managing and Living With Diabetes
Diabetes Tips: Managing and Living With DiabetesIf you have either type 1 or type 2 diabetes, you need to approach life differently. Learn nutrition tips to control blood sugar, ways to manage your insulin, hyperglycemia triggers like stress, and what to do when traveling with diabetes. Discover the various symptoms of diabetes, how they put your body at risk, and steps you can take to live better with diabetes.
 Diabetes Travel: Tips for Better Diabetes Control
Diabetes Travel: Tips for Better Diabetes ControlDiabetes shouldn't stop you from traveling! Learn tips for packing diabetic supplies, controlling blood sugar while changing time zones, as well as improving your airplane travel with diabetes.
 Diabetes: 12 Ways Too Much Sugar Harms Your Body
Diabetes: 12 Ways Too Much Sugar Harms Your BodyThe bitter truth: How too much sugar can harm your physical and mental health.
 Diabetes: 15 Famous Celebrities With Diabetes
Diabetes: 15 Famous Celebrities With DiabetesSee pictures of celebrities that have been diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes including Mary Tyler Moore, Salma Hayek, and Nick Jonas from The Jonas Brothers.
 Diabetes: Best Diets When You Have Diabetes
Diabetes: Best Diets When You Have DiabetesWhich popular eating plans are safe and effective? The right diet will help you control your blood sugar, get a handle on your weight, and feel better. Learn more from this WebMD quiz.
 Diabetes: Best Foods for a Prediabetes Diet
Diabetes: Best Foods for a Prediabetes DietLearn what to eat -- and possibly stop diabetes in in its tracks -- when you’ve been diagnosed with prediabetes.
 Diabetes: Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
Diabetes: Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy TreatmentThis nerve damage is a common complication of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Find out how to prevent it, slow its progression, and deal with symptoms.
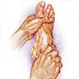 Diabetes: Guide to Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetes: Guide to Diabetic Peripheral NeuropathyDiabetes can damage the nerves that help you feel pain, heat, and cold, especially in your feet. Learn about the symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and the problems it can cause, what you can do about it, and how to prevent it.
 Diabetes: How Blood Sugar Levels Affect Your Body
Diabetes: How Blood Sugar Levels Affect Your BodyHigh blood sugar can be a sign of diabetes or prediabetes. The drugs that treat it sometimes cause low blood sugar too. WebMD helps guide you through the effects of both.
 Diabetes: Low-Carb Choices for Fast Food
Diabetes: Low-Carb Choices for Fast FoodLow carb and fast food don't often go together. Here's how to spot unhealthy carbs and make better choices from the menu.
 Diabetes: What Raises and Lowers Your Blood Sugar Level?
Diabetes: What Raises and Lowers Your Blood Sugar Level?Want to lower your blood sugar? Learn to better control your glucose levels by preventing blood sugar spikes and swings to avoid neuropathy and other diabetes complications. Find foods that lower blood sugar, and identify foods and activities that raise high blood sugar risks.
 Diabetic Neuropathy Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Diabetic Neuropathy Quiz: Test Your Medical IQDiabetic neuropathy is serious. Take this quiz to get the facts.
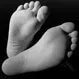 How Diabetes Can Affect Your Feet
How Diabetes Can Affect Your FeetLearn more about diabetes related foot problems. For people with diabetes, too much glucose in the blood can cause serious foot complications such as nerve damage, infection, and ulcers. Find tips for proper foot care to help prevent serious complications.
 Metabolic Syndrome Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Metabolic Syndrome Quiz: Test Your Medical IQMetabolic syndrome is serious and you should be concerned. Learn the causes, symptoms, treatments, and complications of metabolic syndrome with our quick quiz.
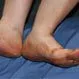 Picture of Peripheral Vascular Disease
Picture of Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDiabetes also affects the blood vessels and alters the flow of blood. See a picture of Peripheral Vascular Disease and learn more about the health topic.
 Prediabetes: You Can Turn It Around
Prediabetes: You Can Turn It AroundPrediabetes can be a wake-up call. Click through to find out what you can do if you have it.
 Slideshow: Diabetes Management in 10 Minutes
Slideshow: Diabetes Management in 10 MinutesLearn 10 simple ways to better manage your diabetes. See tips for controlling blood sugar, diet and exercise and other helpful ideas that cut risk of complications for diabetics.
 Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, Vs. Type 2
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): Symptoms, Causes, Treatments, Vs. Type 2What is type 1 diabetes? There are new treatments for juvenile diabetes, and more people with diabetes can be treated than ever before. Learn the symptoms of T1D, the causes, and find ways to control your blood glucose levels naturally.
 Type 1 Diabetes Quiz: Test Your Medical IQ
Type 1 Diabetes Quiz: Test Your Medical IQWhat are the causes of type 1 diabetes? Take this quiz and challenge your knowledge of causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatments for this common condition, formerly known as juvenile diabetes.
 Type 2 Diabetes: Signs, Symptoms, Treatments
Type 2 Diabetes: Signs, Symptoms, TreatmentsLearn about type 2 diabetes warning signs, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Find out why thirst, headaches, and infections could be signs of diabetes. Discover the treatment options for people with type 2 diabetes, including medicines and lifestyle improvements.
 Type 2 Diabetes: Test Your Medical IQ
Type 2 Diabetes: Test Your Medical IQWhat causes type 2 diabetes? Can it be prevented? Take this online quiz and challenge your knowledge of this common condition. Also, get the truth about myths and facts!
 What You Should Know About Metabolic Syndrome
What You Should Know About Metabolic SyndromeMetabolic syndrome is a group of conditions that happen together that includes high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and high blood sugar, among other things. Find out from WebMD's slideshow if you may be at risk for this serious illness.
Treatment & Diagnosis
Medications & Supplements
- acarbose - oral, Precose
- Actos (pioglitazone)
- Actos (pioglitazone) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- Adlyxin (lixisenatide)
- Adlyxin (lixisenatide) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- alfalfa
- Amaryl (glimepiride)
- Amaryl (glimepiride) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- Avandamet (rosiglitazone/metformin)
- Baqsimi (glucagon)
- becaplermin, Regranex
- bitter melon
- Bydureon Bcise (exenatide)
- calcifediol
- canagliflozin (Invokana)
- captopril - oral, Capoten
- chlorpropamide - oral, Diabinese
- chlorpropamide, Diabinese
- dapagliflozin, Farxiga
- dapagliflozin/metformin
- dapagliflozin/saxagliptin
- empagliflozin
- empagliflozin/linagliptin/metformin hydrochloride
- ertugliflozin/sitagliptin
- exenatide (Byetta)
- gliclazide-oral tablet
- glimepiride - oral, Amaryl
- glipizide (Glipizide XL, Glucotrol)
- glipizide and metformin
- glipizide extended-release tablet - oral, Glucotrol XL
- glipizide tablet - oral, Glucotrol
- glucagon recombinant (GlucaGen)
- glucose (Insta-Glucose, Dex4 & others)
- Glucovance (glyburide/metformin)
- glyburide
- glyburide - oral, Diabeta, Glycron, Glynase, Mic
- Glyxambi (empagliflozin and linagliptin)
- insulin aspart
- insulin aspart - injection, NovoLog
- insulin aspart protamine/insulin aspart - injection, Novolog Mix
- insulin degludec
- insulin degludec and insulin aspart
- insulin detemir
- Insulin for Diabetes Treatment (Types, Side Effects, and Preparations)
- insulin glargine (Lantus)
- insulin lispro - injection, Humalog
- insulin NPH
- insulin regular human
- INSULIN-INJECTION, Humulin, Iletin I NPH, Novolin
- irbesartan - oral, Avapro
- Jardiance (empagliflozin)
- Jardiance Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- L-methylfolate/pyridoxal 5-phosphate/methylcobalamin
- losartan - oral, Cozaar
- magnesium supplement
- mannitol
- metformin
- metformin - oral, Glucophage
- metformin and sitagliptin (Janumet)
- miglitol - oral, Glyset
- miglitol, Glyset
- Mounjaro (tirzepatide)
- nateglinide - oral, Starlix
- pioglitazone - oral, Actos
- Precose (acarbose)
- Regranex (becaplermin) Side Effects, Warnings, and Drug Interactions
- repaglinide (Prandin)
- repaglinide - oral, Prandin
- rosiglitazone (Avandia)
- rosiglitazone - oral, Avandia
- SGLT2 Inhibitors (Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2)
- Side Effects of Avandia (rosigliatazone)
- Side Effects of Byetta (exenatide)
- Side Effects of Diabinese (chlorpropamide)
- Side Effects of Farxiga (dapagliflozin)
- Side Effects of GlucaGen (glucagon)
- Side Effects of Glucophage (metformin)
- Side Effects of Glucotrol (glipizide)
- Side Effects of Glucovance (glyburide/metformin)
- Side Effects of Glyset (miglitol)
- Side Effects of Invokana (canagliflozin)
- Side Effects of Janumet (metformin and sitagliptin)
- Side Effects of Januvia (sitagliptin)
- Side Effects of Lantus (insulin glargine)
- Side Effects of Lyrica (pregabalin)
- Side Effects of Prandin (repaglinide)
- Side Effects of Precose (acarbose)
- Side Effects of Starlix (nateglinide)
- Side Effects of Symlin (pramlintide)
- Side Effects of Tolinase (tolazamide)
- Side Effects of Tradjenta (linagliptin)
- Side Effects of Xultophy (insulin degludec and liraglutide injection)
- sitagliptin (Januvia)
- Starlix (nateglinide)
- Synjardy (empagliflozin and metformin)
- Synjardy XR (empagliflozin and metformin extended-release)
- tolazamide (Tolinase brand has been discontinued.)
- Tradjenta (linagliptin)
- Trulicity (dulaglutide)
- Victoza (liraglutide)
Prevention & Wellness
- Can Nitric Oxide Supplements Help Manage Type 2 Diabetes?
- How Can I Lower My Blood Sugar Quickly and Naturally?
- How Do Artificial Sweeteners Affect Blood Sugar and Insulin?
- Is Brown Sugar Better for Diabetes Than White Sugar?
- The 12 Best Types of Alcohol for People With Diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes Diet
- What Can a Person With Diabetes Eat When Craving Sweets?